PWE3 Carrying HSI Services
HSI Service Overview
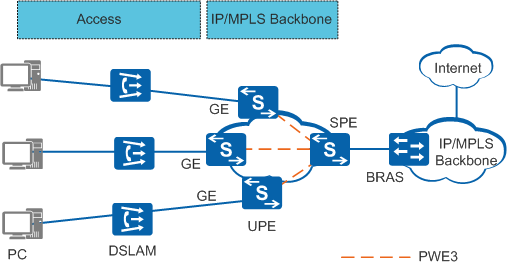
High speed Internet (HSI) services are transmitted over IP networks. Figure 1 shows an example of the HSI service. In Figure 1, data service packets of Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) users are aggregated at Layer 2 and transparently transmitted to the broadband remote access server (BRAS). A Layer 2 connection is established between the BRAS and digital subscriber line access multiplexer (DSLAM) using PWE3. The data service has low requirements for real-time transmission. This networking meets the following conditions on access and bearer networks:
- Strong expansibility
- Clear management responsibilities
- Effective control on Layer 2 broadcast domains
- Guaranteed data security
- Support for multiple protocols and smooth network upgrade
- Ease configuration
Networking Description
In Figure 1, residential HSI services are transmitted in a VLAN on the user-end provider edge (UPE). The UPE connects to the DSLAM and is responsible for aggregating and forwarding traffic of HSI service packets. PWE3 aggregates packets exchanged between the UPE and the network provider edge (NPE). The NPE terminates PWE3 packets and adds VLAN tags to the packets, and sends the packets to the BRAS. The BRAS removes the VLAN tags from packets. The BRAS dynamically assigns an IP address for HSI service users using PPPoE.
PWE3 Deployment
- IP addresses and Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs) are configured on the carrier MPLS backbone network so that PEs can communicate.
- MPLS is enabled on the carrier MPLS backbone network, and TE tunnels are configured between UPEs and NPEs. Usually, two TE tunnels are configured between each UPE and NPE, one as the primary tunnel and the other as the backup tunnel.
- MPLS L2VPN is enabled on each UPE and NPE. A remote MPLS LDP session is configured between each UPE and NPE.
- PWE3 is configured on AC interfaces of each UPE and NPE so that UPEs and NPEs can communicate over MPLS L2VCs.