VLAN Stacking on a VLANIF Interface
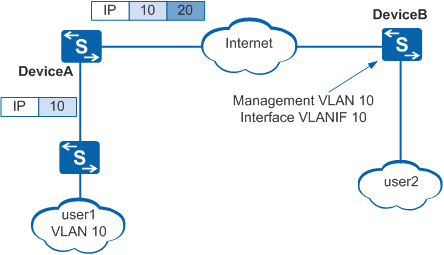
As shown in Figure 1, DeviceA is connected to DeviceB through a third-party network. DeviceB belongs to the management VLAN. The management VLAN ID is the same as the VLAN ID of the downstream user connected to DeviceA but different from the service VLAN (S-VLAN) ID.
To log in to DeviceB and manage VLANs from DeviceA, you can configure VLAN stacking on the VLANIF interface corresponding to the management VLAN on DeviceB.
If the double-tagged packets sent to the carrier network have the same outer VLAN tags as the S-VLAN tag, the packets can be transparently transmitted to DeviceB over the carrier network.
Upon receipt of such a packet on its VLANIF interface, DeviceB compares the VLAN tag with the VLAN tag on the VLANIF interface. If the tags are the same, DeviceB removes the outer VLAN tag and then forwards the packet to the IP layer for processing.
The VLANIF interface on DeviceB adds an outer VLAN tag to received data packets. This tag is the same as the S-VLAN tag. The double-tagged packets can then be transparently transmitted to DeviceA over the carrier network. After receiving the packets, DeviceA removes the outer VLAN tag and then forwards the packets to local users.