Association Between SEP and CFM
Association between SEP and CFM can be configured on the edge devices on a SEP segment. When CFM detects a fault on the network at the aggregation layer, edge devices send CCMs to notify the fault to the Operation, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) module. The SEP status of the interface associated with CFM then changes to Down.
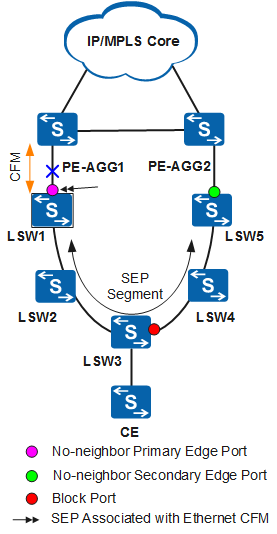
Figure 1 shows a networking diagram of association between SEP and CFM.
In Figure 1, LSW1 to LSW5 run SEP to implement redundancy protection switching at the access layer and display the topology. The interface associated with CFM is in the SEP segment.
When the SEP status of the interface associated with CFM goes Down, LSW2 must send a Flush-FDB packet to notify other nodes of the topology changes. After LSW3 receives the Flush-FDB packet, the blocked interface on LSW3 is unblocked and enters the Forwarding state. The interface sends a Flush-FDB packet to instruct the other nodes to update their MAC address and ARP tables. Therefore, the lower-layer network can then detect the faults on the upper-layer network, ensuring reliable service transmission.