VLL FRR
Widespread adoption of MPLS L2VPNs has raised reliability requirements for L2VPNs, especially for L2VPNs that carry real-time services such as VoIP and IPTV.
Virtual Lease Line Fast Reroute (VLL FRR) uses redundant networking to improve MPLS L2VPN reliability. When a PW or PE device fails, VLL FRR fast switches traffic to a backup link. This mechanism implements end-to-end fault detection on PWs and provides PW protection, greatly improving link-layer reliability for MPLS L2VPNs.
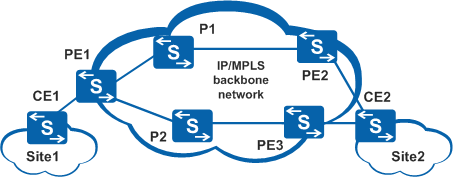
Figure 1 shows the application of VLL FRR in asymmetrical CE deployment: the CE device is connected to one PE device at one end while the CE device is dual-homed to two PE devices at the other end.
In asymmetrical networking, PE1 or CE2 is the failover point and the last step in the fault notification process. When the primary link fails, PE1 in the single-homed site detects the fault, triggers traffic switching, and does not send fault notification to CE1. When the primary link in the dual-homed site fails, CE2 receives the fault notification from the PE device on the primary link and switches traffic to the backup link.
VLL FRR Implementation
Fault Detection
When a fault occurs on the VLL network, devices can detect link failures through route convergence. However, the detection is at a low speed and cannot meet the requirements of delay-sensitive services, such as VoIP. To improve the fault detection speed, Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) is deployed on the PE device to rapidly detect PW failures. BFD has a low cost and achieves millisecond-level fault detection.
Switching Between Primary and Backup PWs
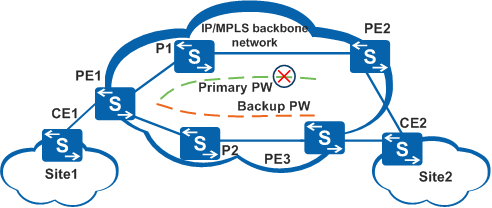
You can set up a backup PW on the VLL network. The backup PW constantly remains in the Up state to ensure traffic can be quickly switched from the primary PW if necessary. If the primary PW is working correctly, the backup PW does not transmit any data. The backup PW is switched to and transmits data only if the primary PW is faulty.
As shown in Figure 2, PE1-P1-PE2 is the primary link and PE1-P2-PE3 is the backup link. When the system detects that the primary PW or PE2 is faulty, PE1 switches between the primary and backup PWs, ensuring traffic transmission from CE1 to CE2.
Fast Fault Notification
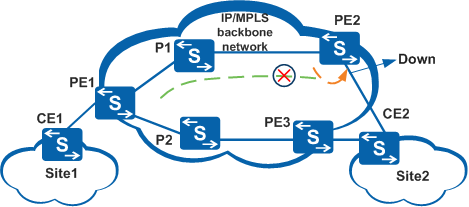
Switching between primary and backup PWs ensures normal traffic transmission from CE1 to CE2, while switching of traffic from CE2 to CE1 is ensured by fast fault notification.
Fault notification on the physical layer implements the transfer of fault information between a PW and an AC. PE2 on the primary PW shuts down the corresponding AC-side interface when it detects a PW failure. CE2 then detects the link failure and triggers link switching, as shown in Figure 3.PW Switchback Policy
On a network where CEs asymmetrically access PEs, when PE1 is notified of fault removal on the primary PW, PE1 works based on the PW switchback policy.
The PW switchback policies are as follows:
No switchback: Traffic is not switched back to the primary PW.
Immediate switchback: Traffic is immediately switched back to the primary PW.
Delayed switchback: Traffic is switched back to the primary PW after a delay period.
After the switchback, the PE immediately notifies the peer PE on the secondary PW of the fault. In addition, after a delay period or immediately the PE notifies the peer PE on the secondary PW of fault removal, which prevents packet loss due to transmission delay between PEs.