Typical Application of an Agile Distributed WLAN
In scenarios with a high concentration of rooms, such as hotels, school dormitories, and hospitals, walls or other indoor objects may cause severe signal attenuation. Common indoor settled APs or distributed APs cannot meet the requirement of high-performance wireless coverage at low costs; therefore, Huawei develops the agile distributed WLAN architecture.
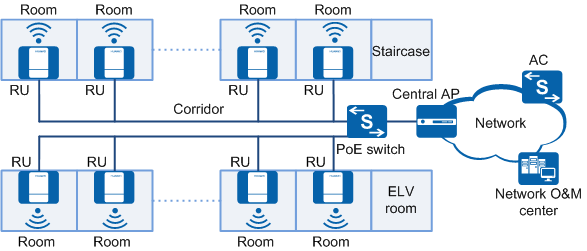
An agile distributed WLAN is composed of the AC, central AP, and RU. The RU receives and sends wireless packets. The central AP connects to the RUs through network cables. Compared with feeder cables used by common APs to connect to antennas, the network cables provide longer deployment distance, allowing RUs to be deployed further from the central AP.
The central AP directly connects to RUs and provides PoE power for RUs, as shown in Figure Figure 1. You can also connect the central AP to RUs through a switch to increase the number of the connected RUs. A Layer 2 reachable tree network must be deployed between the RUs and central AP.
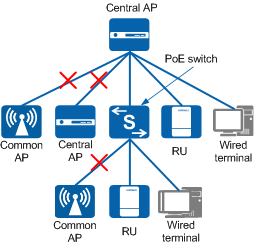
In addition to RUs, the central AP can connect to wired terminals in the downlink direction. However, it cannot connect to common APs or other central APs, as shown in Figure 2. When the central AP connects to wired terminals, the wired terminals do not support 802.1X authentication because the central AP cannot transparently transmit EAP packets. Therefore, authentication packets of wired terminals cannot reach the uplink authentication point through the central AP.