Understanding Wi-Fi Tag Location
Concepts
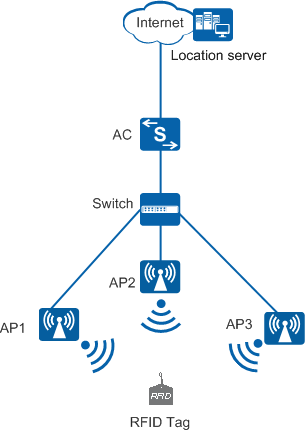
As shown in Figure 1, the tag location system includes at least three APs, one or more Wi-Fi tags, one or more ACs, a location server, and a location display terminal. Functions of each component are as follows:
- Wi-Fi tag: is manufactured by tag vendors to generate signals. For example, AeroScout manufactures Wi-Fi tags that are often placed or pasted to the objects to be located. The tag is a source device that needs to be located and can periodically send radio waves to surrounding devices.
- AP: receives location information sent by a Wi-Fi tag and forwards the information to the AC or directly sends it to a location server.
- AC: forwards the configuration instruction from the location server to APs. It can also forward location information received from an AP to the location server.
- Location server: computes the Wi-Fi tag location using a location algorithm (for example, three-point location) after receiving the location information, and provides the computed data to user systems, including the system management software and image software.
Implementation
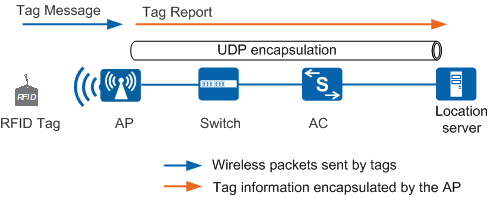
Figure 2 shows how wireless location is implemented.
The Wi-Fi tag sends a tag message.
The Wi-Fi tag only sends 802.11 frames periodically to provide location information and does not need to connect to a WLAN.
To enable more APs to receive tag messages, the Wi-Fi tag sends a tag message in all channels each time. A tag message usually contains location information required by a location server, and the frame format of the tag message varies depending on the vendor's tag device.
The AP receives the tag message and forwards it to the location server.
- When receiving a tag message frame, the AP records the location information such as the received signal strength indicator (RSSI), timestamp, rate, and channel of the frame. The RSSI is the most important information because the location server uses it to determine the distance between a tag and an AP. To ensure that the RSSI is accurate, the AP must filter out the tag messages received from adjacent channels. For example, when working in channel 1, the AP may receive the frames sent from a tag in channel 2. The RSSI is low because the AP and tag are located in different channels. As a result, the location server incorrectly considers that the tag is far away from the AP.
- The AP encapsulates all location information obtained from tag message frames into a UDP packet (tag report) and sends the packet to the location server directly or through the AC.
The required location information and report mode vary depending on the vendor's location server. For example, the Ekahau Location Server requires that the location information should contain content of the tag message frames and the AP should report tag message frames immediately when receiving them; the AeroScout Location Server does not need content of the tag message frames and allows the AP to periodically report collected location information.
The destination IP address and port number of a tag report packet are configured on the AC. If the destination address is set to the IP address of the location server, the tag report packet is directly sent to the location server. If the destination address is set to the AC IP address, the tag report packet is sent to the AC and forwarded by the AC to the location server. This configuration is used when the AP cannot be directly connected to the location server.
The location server computes the location information.
To accurately determine the tag location, the location server must receive location information about a tag from at least three APs. After receiving the tag information, the location server uses the built-in computing algorithm to compute the tag location according to information including the RSSI, SNR, radio mode, the imported map, and AP locations. Then, the location server sends the location information to the graphical interface of the third-party device for presentation.