WMM
Background
It is vital to understand the 802.11 link layer transport mechanism before learning about WMM.
- Distributed Coordination Function (DCF): uses the carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) mechanism. STAs compete for channels to obtain the authority to transmit data frames.
- Point Coordination Function (PCF): uses centralized control to authorize STAs to transmit data frames in turn. This method prevents conflict.

In the 802.11 protocol, DCF is mandatory, and PCF is optional.
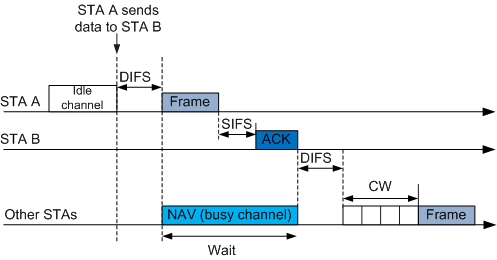
- Before sending data to STA B, STA A detects the channel status. When detecting an idle channel, STA A sends a data frame after Distributed Inter-Frame Space (DIFS) times out and waits for a response from STA B. The data frame contains NAV information. After receiving the data frame, STA B updates the NAV information, indicating that the channel is busy and that data transmission will be delayed.

According to the 802.11 protocol, the receiver must return an ACK frame each time it receives a data frame.
- STA B receives the data frame, waits until Short Interframe Space (SIFS) times out, and sends an ACK frame to STA A. After the ACK frame is transmitted, the channel becomes idle. After the DIFS times out, the STAs use the exponential backoff algorithm to compete for channels. The STA of which the backoff counter is first reduced to 0 starts to send data frame.
Concepts
- InterFrame Space (IFS): According to the 802.11 protocol, after sending a data frame, the STA must wait until the IFS times out to send the next data frame. The IFS length depends on the data frame type. High-priority data frames are sent earlier than low-priority data frames. There are three IFS types:
- Short IFS (SIFS): The time interval between a data frame and its ACK frame. SIFS is used for high priority transmissions, such as ACK and CTS frame transmissions.
- PCF IFS (PIFS): PIFS length is SIFS plus slot time. PCF-enabled access points wait for the duration of PIFS to occupy the wireless medium. If a STA accesses a channel when the slot time starts, the other STAs in the BSS detect that the channel is busy.
- DCF IFS (DIFS): DIFS length is PIFS plus slot time. Data frames and management frames are transmitted at the DIFS interval.
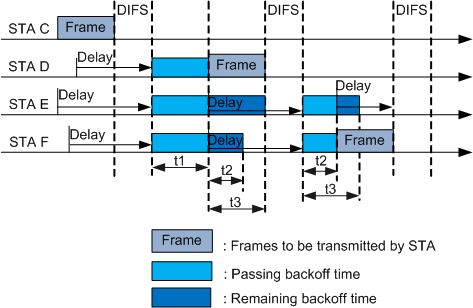
Contention window: backoff time. Backoff time is a multiple of slot time, and its length depends on the physical layer technology. When multiple STAs need to transmit data but detect that all channels are busy, the STAs use the backoff algorithm. The STAs wait for a random number of slot times, and then transmit data. A STA detects channel status during the slot time interval. When detecting an idle channel, the STA starts the backoff timer. If all channels become busy, the STA freezes the remaining time in the backoff timer. When a channel becomes idle, the STA waits until DIFS times out, and continues the backoff timer. When the backoff timer is reduced to 0, the STA starts to send data frames. Figure 2 shows the data frame transmission process.
- STA C is occupying a channel to send data frames. STA D, STA E, and STA F also need to send data frames. They detect that the channel is busy and wait.
- After STA C finishes data frame transmission, the other STAs wait until DIFS times out. When DIFS times out, the STAs generate a random backoff time and start their backoff timers. For example, the backoff time of STA D is t1, the backoff time of STA E is t1+t3, and the backoff time of STA F is t1+t2.
- When t1 times out, the backoff timer of STA D is reduced to 0. STA D starts to send data frames.
- STA E and STA F detect that the channel is busy, so they freeze their backoff timers and wait. After STA D completes data transmission, STA E and STA F wait until DIFS times out, and continue their backoff timers.
- When t2 times out, the backoff timer of STA F is reduced to 0. STA F starts to send data frames.
Principles
Channel competition is based on DCF. To all STAs, the DIFS is fixed and backoff time is random. Therefore, all the STAs fairly compete for channels. WMM enhances the 802.11 protocol, changing the channel competition mode.
EDCA parameters
WMM defines a set of Enhanced Distributed Channel Access (EDCA) parameters, which distinguishes high priority packets and enables these packets to preempt channels.
WMM classifies data packets into four access categories (ACs). Table 1 shows the mappings between ACs and 802.11 user preferences (UPs).Each AC queue defines a set of EDCA parameters, which determines the capability of occupying channels. These parameters ensure that high priority ACs have a higher probability of preempting channels than low priority ones.
Table 2 describes the EDCA parameters.Table 2 EDCA parameter description Parameter
Meaning
Arbitration Interframe Spacing Number (AIFSN)
The DIFS has a fixed value. WMM provides different DIFS values for different ACs. A large AIFSN value means that the STA must wait for a long time and has a low priority.
Exponent form of CWmin (ECWmin) and exponent form of CWmax (ECWmax)
ECWmin specifies the minimum backoff time, and ECWmax specifies the maximum backoff time. Together, they determine the average backoff time. Large ECWmin and ECWmax values mean a long average backoff time for the STA and a low STA priority.
Transmission Opportunity Limit (TXOPLimit)
After preempting a channel, the STA can occupy the channel within the period of TXOPLimit. A large TXOPLimit value means that the STA can occupy the channel for a long time. If the TXOPLimit value is 0, the STA can only send one data frame every time it preempts a channel.
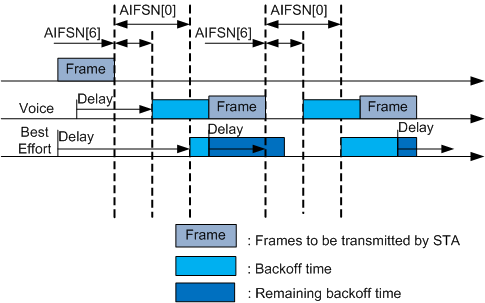
As shown in Figure 3, the AIFSN (AIFSN[6]) and the backoff time of voice packets are shorter than those of Best Effort packets. When both voice packets and Best Effort packets need to be sent, voice packets preempt the channel.
ACK policy
WMM defines two ACK policies: normal ACK and no ACK.
Normal ACK: The receiver must return an ACK frame each time it receives a unicast packet.
No ACK: The receiver does not need to return ACK frames after receiving packets. This mode is applicable to environments with high communication quality and little interference.

- The ACK policy is only valid to APs.
- If communication quality is poor, the no ACK policy may cause more packets to be lost.