Uninterrupted AP Operation After CAPWAP Link Disconnection
In an AC + Fit AP network architecture, management packets between the AC and APs are forwarded through CAPWAP links. When the CAPWAP links are faulty, original STAs connected to an AP are forced to go offline and new STAs cannot access the AP. In a tunnel forwarding scenario, management and service packets must pass through the CAPWAP links. As a result, if the CAPWAP links are disconnected, service packets of STAs are interrupted and cannot be restored. However, in a direct forwarding scenario, service packets do not need to pass through the CAPWAP links. In this case, you can configure an escape policy to enable the AP to continue providing WLAN services, so that services of online STAs are not interrupted and new STAs can access the AP.
Service holding upon CAPWAP link disconnection
After the service holding function is enabled, the AP can still forward data packets when the CAPWAP tunnel is faulty. This function ensures uninterrupted data service transmission in direct forwarding mode, reducing loss for users and improving service reliability.
Figure 1 Service holding upon CAPWAP link disconnection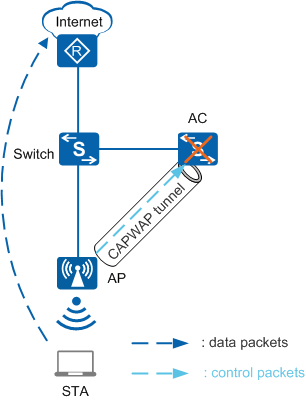
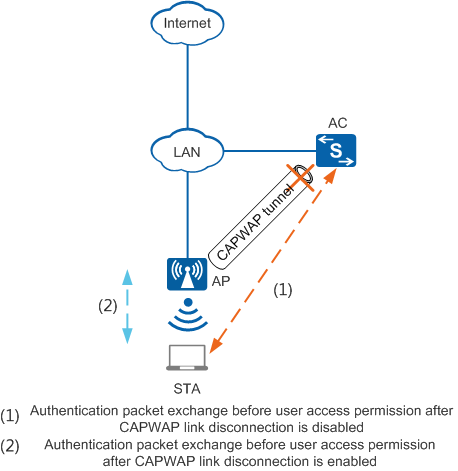
User access permission after CAPWAP link disconnection
The service holding function takes effect only for online users but not for offline users. Under normal circumstances, offline users are not allowed to go online when the CAPWAP link is broken.
When the function that allows STA access after CAPWAP link disconnection is enabled, the AP allows offline STAs to go online and access the network. After the broken CAPWAP link is restored, the AP forces all the STAs that went online during CAPWAP link disconnection to go offline. The AP then reassociates with these STAs and reports STA information through logs. For Portal or MAC address authentication STAs, after the broken CAPWAP link is restored, the AP forces all these STAs to go offline and reports STA information through logs.

This function takes effect only when the WLAN uses open system authentication, Portal authentication, MAC address authentication, WEP authentication, or WPA/WPA2–PSK authentication.
This function allows all the users who enter the correct key to go online. The STA whitelist and blacklist configured on the AC do not take effect after the CAPWAP link is broken.
When the function that allows user access after CAPWAP link disconnection is disabled, STA association and key negotiation are performed between the AC and STA. After this function is enabled, STA authentication, association, and key negotiation are performed between the AP and STA. The different processes for association and authentication are shown in Figure 2.
On an agile distributed WLAN, the service holding or user access permission functions apply only to scenarios where the CAPWAP link between the AC and central AP is disconnected but not to scenarios where the CAPWAP link between the central AP and RU is disconnected.