Overview of Roaming
Definition
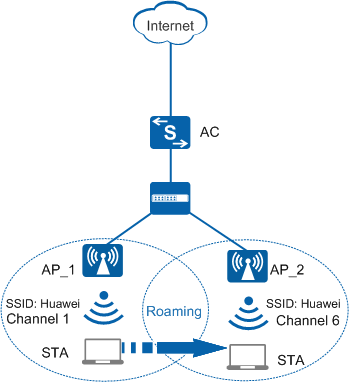
WLAN roaming allows a STA to move from an AP to another AP in the same ESS on a WLAN network with nonstop service transmission. In Figure 1, the STA moves from AP_1 to AP_2.
- Roaming between APs in the same service VLAN: APs before and after STA roaming belong to the same service VLAN.
- Roaming between APs in different service VLANs: APs before and after STA roaming belong to different service VLANs. To prevent services of a user from being interrupted during WLAN roaming, ensure that the service VLAN of the user remains unchanged after the user roams between two APs.
Comparison of WLAN roaming modes
| Roaming Mode | Whether the STA Support Is Required | Applied Security Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Common roaming | Not involved | All security policies |
| PMK fast roaming | Yes | WPA2–802.1X |
| 802.11r roaming | Yes | Open system authentication/WPA2–PSK/WPA2–802.1X |
| Roaming Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| Common roaming | It is applicable to all scenarios and allows for easy configuration. Services may be interrupted for a short period of time during roaming. |
| PMK fast roaming | It is applicable to a few scenarios. During roaming, users do not need to perform 802.1X authentication again and only need to perform key negotiation. The latency is low. |
| 802.11r roaming | It is applicable to multiple scenarios. During roaming, users do not need to perform authentication or key negotiation. The latency is low. |
Purpose
The biggest advantage of WLAN networks is that a STA can move within a WLAN network regardless of physical media locations. WLAN roaming ensures that a STA moves within a WLAN network without interrupting services. An ESS includes multiple APs. When a STA moves from an AP to another AP, WLAN roaming ensures seamless transition of STA services between APs.
Prevents packet loss or service interruption caused by long-term authentication.
If a STA needs to be authenticated before accessing the Internet, the authentication process (for example, 802.1X authentication) may take a long period of time. Fast roaming prevents STA re-authentication, ensuring nonstop user service transmission.
Ensures that users' IP addresses remain unchanged.
Application protocol packets are transmitted using IP addresses and TCP/UDP connections. STAs' IP addresses must remain unchanged after WLAN roaming so that the TCP/UDP connections established for the STAs are not interrupted.