BGP Route Selection Rules and Load Balancing

The switch currently does not support the AIGP attribute.
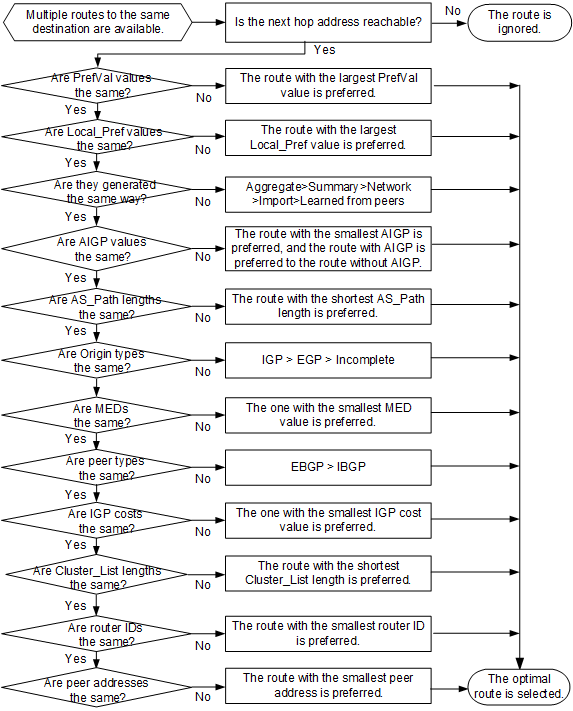
BGP selects routes by comparing route attributes in a fixed order. When a route attribute is a sufficient condition for determining the optimal route, BGP does not compare the other attributes; If BGP fails to select the optimal route after comparing all route attributes, the route that was first received is selected as the optimal route. Table 1 lists the abbreviated alias, route selection rules, and remarks of each matching item. Table 1 shows that the route priority is directly proportional to the PreVal or Local_Pref value and inversely proportional to the rest of the attribute values or lengths. In addition, the first column can be summarized as a character string (PPAAA OMTCC RA), which helps memorize the matching sequence.
Abbreviated Alias |
Matching Item |
Route Selection Rules |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
P |
PrefVal |
The route with the largest PreVal value is preferred. The default value is 0. |
PrefVal is Huawei-specific and valid only on the device where it is configured. |
P |
Local_Pref |
The route with the largest Local_Pref value is preferred. The default value is 100. |
To modify the default Local_Pref value of BGP routes, run the default local-preference command. |
A NOTE:
A is the initial of the character string (ASNIL). |
Route type |
A > S > N > I > L, in which:
|
- |
A |
Accumulated Interior Gateway Protocol (AIGP) |
The route with the smallest AIGP value is preferred. The route with AIGP to the route without AIGP is preferred. |
- |
A |
AS_Path |
The route with the shortest AS_Path length is preferred. |
If the bestroute as-path-ignore command is configured, BGP does not compare the AS_Path attribute. |
O |
Origin |
IGP > EGP > Incomplete |
- |
M |
Multi Exit Discriminator (MED) |
The route with the smallest MED value is preferred. The default value is 0. |
If the bestroute med-none-as-maximum command is configured, BGP considers the largest MED value (4294967295) as the MED of the route that does not carry an MED. |
T |
Peer type |
EBGP > IBGP |
Prefers EBGP routes, IBGP routes, LocalCross routes, and RemoteCross routes, which are listed in descending order of priority. LocalCross allows a PE to add the VPNv4 route of a VPN instance to the routing table of the VPN instance if the export RT of the VPNv4 route matches the import RT of another VPN instance on the PE. RemoteCross allows a local PE to add the VPNv4 route learned from a remote PE to the routing table of a VPN instance on the local PE if the export RT of the VPNv4 route matches the import RT of the VPN instance. |
C |
IGP cost |
The route with the smallest IGP cost is preferred. |
If there are multiple routes to the same destination, an IGP calculates the route metric using its routing algorithm. If the bestroute igp-metric-ignore command is configured, BGP does not compare the IGP cost. |
C |
Cluster_List |
The route with the shortest Cluster_List length is preferred. |
By default, Cluster_List takes precedence over Originator_ID during BGP route selection. To enable Originator_ID to take precedence over Cluster_List during BGP route selection, run the bestroute routerid-prior-clusterlist command. |
R |
Router ID |
The route with the smallest router ID is preferred. |
If routes carry the Originator_ID, the originator ID is substituted for the router ID during route selection. The route with the smallest Originator_ID is preferred. |
A |
Peer IP address |
The route learned from the peer with the smallest IP address is preferred. |
- |
Selection of the Routes for Load Balancing
After BGP load balancing is configured, the BGP routes that meet the following conditions are used as equal-cost routes for load balancing:
The routes have the same PrefVal value.
The routes have the same Local_Pref value.
All the routes are summarized or non-summarized routes.
The routes have the same AIGP value.
The routes have the same AS_Path length.
The routes have the same origin type (IGP, EGP, or incomplete).
The routes have the same MED value.
All the routes are EBGP or IBGP routes. After the maximum load-balancing eibgp command is run, BGP ignores this limitation when selecting the optimal VPN route.
The costs of the IGP routes to which the BGP routes are iterated within an AS are the same. After the maximum load-balancing eibgp command is run, BGP ignores this limitation when selecting the optimal VPN route.
In addition, BGP labeled routes and non-labeled routes cannot load-balance traffic even if they meet the preceding conditions.
VPN Route Selection Rules
BGP VPN routes are selected in the same way as BGP public routes except that VPN target-based route crossing is implemented first on BGP VPN routes.