PrefVal
PrefVal is Huawei-specific and valid only on the device where it is configured. The PreVal attribute is set by customers. Therefore, BGP first compares the PreVal values during route selection.
If multiple routes are available to the same destination, the route with the largest PreVal value is selected as the optimal route. By default, the PreVal of the routes learned from BGP peers is 0.
Method |
Usage Scenario |
|---|---|
Run the peer { group-name | ipv4-address | ipv6-address } preferred-value value command. |
This method sets a PreVal value for the routes learned from a peer or peer group. |
Configure an import policy and run the apply preferred-value preferred-value command to configure an apply clause for the policy. |
This method sets different PreVal values for different routes learned from a peer or peer group. NOTE:
If both the methods are used, the method with the import policy takes effect if routes match the conditions specified in the peer preferred-value command and the import policy. |
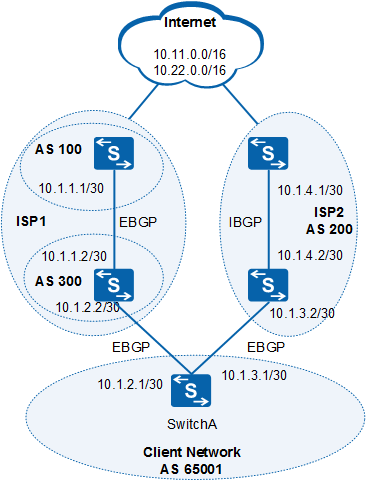
Scenario 1: When no PreVal value is configured on Switch A, check the BGP routing table of Switch A.
[HUAWEIA] display bgp routing-table
BGP Local router ID is 10.1.2.1
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped,
h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale
Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Total Number of Routes: 4
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
*> 10.11.0.0/16 10.1.3.2 0 200?
* 10.1.2.2 0 300 100?
*> 10.22.0.0/16 10.1.3.2 0 200?
* 10.1.2.2 0 300 100?
The BGP routing table of Switch A shows that Switch A receives the routes 10.11.0.0/16 and 10.22.0.0/16 from ISP1 and ISP2. Check the information about the route 10.11.0.0/16 on Switch A.
[HUAWEIA] display bgp routing-table 10.11.0.0
BGP local router ID : 10.1.2.1
Local AS number : 65001
Paths: 2 available, 1 best, 1 select
BGP routing table entry information of 10.11.0.0/16:
From: 10.1.3.2 (10.1.3.2)
Route Duration: 00h08m35s
Direct Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Original nexthop: 10.1.3.2
Qos information : 0x0
AS-path 200, origin incomplete, pref-val 0, valid, external, best, select, active, pre 255
Advertised to such 2 peers:
10.1.3.2
10.1.2.2
BGP routing table entry information of 10.11.0.0/16:
From: 10.1.2.2 (10.1.2.2)
Route Duration: 00h04m38s
Direct Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/0
Original nexthop: 10.1.2.2
Qos information : 0x0
AS-path 300 100, origin incomplete, pref-val 0, valid, external, pre 255, not preferred for AS-Path
Not advertised to any peer yet
Route Attribute |
Route Learned from ISP1 |
Route Learned from ISP2 |
Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
PrefVal |
0 |
0 |
The same. |
Local_Pref |
- |
- |
The same. NOTE:
If a route does not carry Local_Pref, the default value 100 takes effect. |
Route type |
Learned from a peer |
Learned from a peer |
The same. |
AIGP |
- |
- |
The same. |
AS_Path |
300 100 |
200 |
The route learned from ISP2 is selected as the optimal route because its AS_Path is shorter than that of the route learned from ISP1. |
Scenario 2: The administrator of AS 65001 requires that ISP1 be active and ISP2 be backup for the traffic to 10.11.0.0/16 and 10.22.0.0/16.
To meet the preceding requirements, run the peer { group-name | ipv4-address | ipv6-address } preferred-value value command on Switch A to increase the PrefVal values of the routes learned from ISP1. This configuration ensures that the routes learned from ISP1 are selected as the optimal routes. Detailed configurations are as follows:
bgp 65001 # ipv4-family unicast peer 10.1.2.2 preferred-value 120 //Set the PrefVal of the routes learned from AS 300 to 120.
Run the display bgp routing-table [ ip-address ] command to check the configurations.
# Display the routing table of Switch A.
[HUAWEIA] display bgp routing-table
BGP Local router ID is 10.1.2.1
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped,
h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale
Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Total Number of Routes: 4
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
*> 10.11.0.0/16 10.1.2.2 120 300 100?
* 10.1.3.2 0 200?
*> 10.22.0.0/16 10.1.2.2 120 300 100?
* 10.1.3.2 0 200?
The preceding command output shows that Switch A selects the routes learned from ISP1.
# Display detailed information about the route 10.11.0.0/16 or 10.22.0.0/16 on Switch A. The route 10.11.0.0/16 is used as an example.
[HUAWEIA] display bgp routing-table 10.11.0.0
BGP local router ID : 10.1.2.1
Local AS number : 65001
Paths: 2 available, 1 best, 1 select
BGP routing table entry information of 10.11.0.0/16:
From: 10.1.2.2 (10.1.2.2)
Route Duration: 00h05m36s
Direct Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/0
Original nexthop: 10.1.2.2
Qos information : 0x0
AS-path 300 100, origin incomplete, pref-val 120, valid, external, best, select, active, pre 255
Advertised to such 2 peers:
10.1.3.2
10.1.2.2
BGP routing table entry information of 10.11.0.0/16:
From: 10.1.3.2 (10.1.3.2)
Route Duration: 00h23m11s
Direct Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Original nexthop: 10.1.3.2
Qos information : 0x0
AS-path 200, origin incomplete, pref-val 0, valid, external, pre 255, not preferred for PreVal
Not advertised to any peer yet
The preceding command output shows that the PrefVal value of the route learned from ISP1 is greater than that of the route learned from ISP2 and that the route learned from ISP1 is selected as the optimal route.
Scenario 3: The expected configurations of the administrator of AS 65001 are as follows:
- For the traffic destined to 10.11.0.0/16, ISP1 is active and ISP2 is backup.
- For the traffic destined to 10.22.0.0/16, ISP2 is active and ISP1 is backup.
To meet the preceding requirements, ensure that Switch A selects the route 10.11.0.0/16 learned from ISP1 and the route 10.22.0.0/16 learned from ISP2. In this situation, the peer preferred-value command can no longer be used because different PrefVal values are required for the routes learned from the same ISP. To allow different PrefVal values for the routes learned from the same ISP, configure import policies. Detailed configurations are as follows:
# bgp 65001 # ipv4-family unicast peer 10.1.2.2 route-policy for_isp1_in import //Apply import policy named for_isp1_in to the routes learned from 10.1.2.2 and use for_isp1_in to modify the PrefVal value. peer 10.1.3.2 route-policy for_isp2_in import //Apply import policy named for_isp2_in to the routes learned from 10.1.3.2 and use for_isp2_in to modify the PrefVal value. # route-policy for_isp1_in permit node 10 //Define the first node of for_isp1_in and set the PrefVal value of the route 10.11.0.0/16 to 80. if-match ip-prefix for_isp1 apply preferred-value 80 # route-policy for_isp1_in permit node 20 //Define the second node of for_isp1_in and allow for_isp1_in to permit all routes. # route-policy for_isp2_in permit node 10 //Define the first node of for_isp2_in and set the PrefVal value of the route 10.22.0.0/16 to 120. if-match ip-prefix for_isp2 apply preferred-value 120 # route-policy for_isp2_in permit node 20 //Define the second node of for_isp2_in and allow for_isp2_in to permit all routes. # ip ip-prefix for_isp1 index 10 permit 10.11.0.0 16 //Configure an IP prefix list to match the route 10.11.0.0/16. ip ip-prefix for_isp2 index 10 permit 10.22.0.0 16 //Configure an IP prefix list to match the route 10.22.0.0/16. #
Run the display bgp routing-table [ ip-address ] command to check the configurations.
# Display the routing table of Switch A.
[HUAWEIA] display bgp routing-table
BGP Local router ID is 10.1.2.1
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped,
h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale
Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Total Number of Routes: 4
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
*> 10.11.0.0/16 10.1.2.2 80 300 100?
* 10.1.3.2 0 200?
*> 10.22.0.0/16 10.1.3.2 120 200?
* 10.1.2.2 0 300 100?
The preceding command output shows that Switch A selects the route 10.11.0.0/16 learned from ISP1 and the route 10.22.0.0/16 learned from ISP2.
# Display detailed information about the route 10.22.0.0/16 on Switch A.
[HUAWEIA] display bgp routing-table 10.22.0.0
BGP local router ID : 10.1.2.1
Local AS number : 65001
Paths: 2 available, 1 best, 1 select
BGP routing table entry information of 10.22.0.0/16:
From: 10.1.3.2 (10.1.3.2)
Route Duration: 00h14m14s
Direct Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Original nexthop: 10.1.3.2
Qos information : 0x0
AS-path 200, origin incomplete, pref-val 120, valid, external, best, select, active, pre 255
Advertised to such 2 peers:
10.1.3.2
10.1.2.2
BGP routing table entry information of 10.22.0.0/16:
From: 10.1.2.2 (10.1.2.2)
Route Duration: 00h07m54s
Direct Out-interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/0
Original nexthop: 10.1.2.2
Qos information : 0x0
AS-path 300 100, origin incomplete, pref-val 0, valid, external, pre 255, not preferred for PreVal
Not advertised to any peer yet
The preceding command output shows that two routes 10.22.0.0/16 are available in the BGP routing table of Switch A and that the route with the next hop address 10.1.3.2 is selected because its PrefVal (120) is greater than the PrefVal (0) of the route with next hop address 10.1.2.2. The PrefVal value is sufficient enough to determine the optimal route, and therefore, Switch A does not compare other route attributes.
The preceding examples show that PrefVal values can be configured as required to control the traffic forwarding path.