IGP Cost
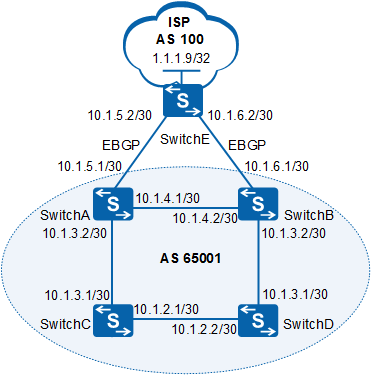
Run the display bgp routing-table [ ip-address ] command on Switch C and Switch D to check the configurations. Switch C is used as an example.
# Display the routing table of Switch C.
[HUAWEIC] display bgp routing-table
BGP Local router ID is 10.1.1.1
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped,
h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale
Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Total Number of Routes: 4
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
*>i 1.1.1.9/32 10.1.5.2 0 100 0 100i
* i 10.1.6.2 0 100 0 100i
*>i 10.1.5.0/30 10.1.3.2 0 100 0 i
*>i 10.1.6.0/30 10.1.2.2 0 100 0 i
The preceding command output shows that two routes 1.1.1.9/32 are available in the routing table of Switch C and that Switch C selects the route learned from Switch A.
[HUAWEIC] display bgp routing-table 1.1.1.9
BGP local router ID : 10.1.1.1 Local AS number : 65001 Paths: 2 available, 1 best, 1 select BGP routing table entry information of 1.1.1.9/32: From: 10.1.3.2 (2.2.2.9) Route Duration: 00h00m44s Relay IP Nexthop: 10.1.3.2 Relay IP Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/0 Original nexthop: 10.1.5.2 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path 100, origin igp, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, best, select, active, pre 255 Not advertised to any peer yet BGP routing table entry information of 1.1.1.9/32: From: 10.1.2.2 (10.1.2.2) Route Duration: 00h00m39s Relay IP Nexthop: 10.1.1.2 Relay IP Out-Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/1 Original nexthop: 10.1.6.2 Qos information : 0x0 AS-path 100, origin igp, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, pre 255, IGP cost 2, not preferred for IGP cost Not advertised to any peer yet
The preceding command output shows that the route with next hop address 10.1.6.2 is ignored because its IGP cost is larger than that of the other route. Table 1 describes the attribute comparison of the routes learned from Switch A and Switch B.
Route Attribute |
Route Learned from Switch A |
Route Learned from Switch B |
Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
PrefVal |
0 |
0 |
The same. |
Local_Pref |
100 |
100 |
The same. |
Route type |
Learned from a peer |
Learned from a peer |
The same. |
AIGP |
- |
- |
The same. |
AS_Path |
100 |
100 |
The same length. |
Origin |
IGP |
IGP |
The same. |
MED |
0 |
0 |
The same. |
Peer type |
IBGP |
IBGP |
The same. |
IGP cost |
- |
2 |
The route learned from Switch A is optimal. NOTE:
If a BGP route carries no IGP cost value, BGP considers
its IGP cost to be 0. If no IGP routes are used during BGP peer relationship
establishment or the costs of used IGP routes are 0, the IGP cost
is not displayed in the display bgp routing-table ip-address command output. |