Route Convergence
Definition
Route convergence is the action of recalculating routes to replace existing routes in the case of network topology changes. The integration of multiple network services urgently requires differentiated services. Routes for key services, such as Voice over IP (VoIP), video conferences, and multicast services, need to be converged rapidly, while routes for common services can be converged relatively slowly. In this case, the system needs to converge routes based on their convergence priorities to improve network reliability.
Priority-based convergence is a mechanism that allows the system to converge routes based on the convergence priority. You can set different convergence priorities for routes: critical, high, medium, and low (in descending order of priority). The system then converges routes based on the convergence priorities and certain convergence rules, that is, schedules these routes in proportion, to guide service forwarding.
Principles
Routing protocols first compute and deliver routes of high convergence priority to the system. You can reconfigure the scheduling weight values as required. Table 1 lists the default convergence priorities of public routes.
Routing Protocol or Route Type |
Convergence Priority |
|---|---|
Direct |
high |
Static |
medium |
32-bit host routes of OSPF and IS-IS |
medium |
OSPF routes (excluding 32-bit host routes) |
low |
IS-IS routes (excluding 32-bit host routes) |
low |
RIP |
low |
BGP |
low |

For private routes, only the convergence priorities of 32-bit OSPF and IS-IS host routes are identified as medium, and the convergence priorities of the other routes are identified as low.
Priority-based Route Convergence
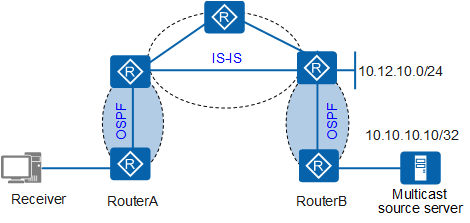
Figure 1 shows a networking arrangement for multicast services. OSPF and IS-IS run on the network. The receiver connects to RouterA, and the multicast source server 10.10.10.10/32 connects to RouterB. The route to the multicast source server must be converged faster than other routes such as 10.12.10.0/24. You can set the convergence priority of route 10.10.10.10/32 to be higher than that of route 10.12.10.0/24. When routes are converged on the network, the route to the multicast source server 10.10.10.10/32 is converged first. This ensures the transmission of multicast services.