IS-IS Overload
IS-IS Overload allows a device to use the IS-IS overload bit to identify the overload state. The IS-IS overload bit is the OL field in an IS-IS LSP. After the overload bit is set on a device, other devices ignore this device when performing SPF calculation and consider only the direct routes of the device.
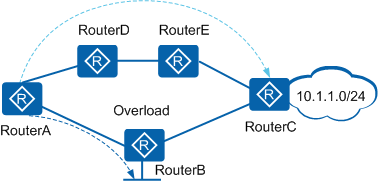
As shown in Figure 1, RouterB forwards the packets sent from RouterA to network segment 10.1.1.0/24. If the overload bit in the LSP sent from RouterB is set to 1, RouterA considers the LSDB of RouterB incomplete and sends packets to 10.1.1.0/24 through RouterD and RouterE. This process does not affect the packets sent to the directly connected network segment of RouterB.
If a device cannot store new LSPs and fails to synchronize the LSDB, the routes calculated by this device are incorrect. In this situation, the device enters the overload state and does not calculate the routes passing through this device; however, the direct routes of the device are still valid.

- If the system enters the overload state because of an abnormality, the system deletes all the imported or leaked routes.
- If the system is configured to enter the overload state, the system determines whether to delete all the imported or leaked routes based on the configuration.