AS Access User Authentication Configuration

If access users do not need to be authenticated, skip this section.
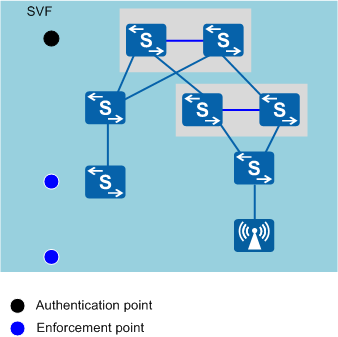
In an SVF system shown in Figure 1, the parent functions as the access control authentication point of all users, and so services of the authentication server only need to be configured on the parent once, simplifying deployment. The access control enforcement points of all users are deployed on ASs. To ensure security, users who fail authentication cannot access ASs.
An SVF system supports three access user authentication modes: MAC, 802.1X, and Portal. Table 1 lists the characteristics and application scenarios of the three authentication modes.
Authentication Mode |
Characteristics |
Applicable Scenario |
|---|---|---|
MAC |
|
Dumb terminals, such as printers and fax machines, need to connect to the network. |
802.1X |
|
The network is newly built, users are densely distributed, and high information security is required. |
Portal |
|
Users are sparsely distributed or move freely. |
An SVF system supports only one combination of authentication modes. The combination can contain one or more of MAC, 802.1X, and Portal authentication modes according to scenario requirements.
- Wired access terminal authentication scenario
- Wired access terminal authentication mode
Table 2 Recommended authentication modes in a wired access terminal authentication scenario Scenario
Scenario Characteristics
Typical Terminal
Recommended Authentication Mode
Remarks
Campus office network
- The network is closed, users seldom change their locations, and high security is required.
- Locations of some laptops may change. For example, these laptops are moved from offices to meeting rooms or moved between departments.
- A few dumb terminals such as printers exist.
Laptops and printers
802.1X
- Configure dumb terminals such as printers as static users on the parent.
- Configure 802.1X authentication on all AS ports to which access terminals are connected.
- Use centralized forwarding of user traffic and UCL to implement inter-departmental user isolation.
Educational institution
- The network is closed, and terminals are densely distributed.
- Locations of wired terminals seldom change, and communication between local users generally does not need to be restricted.
Laptops
Portal
If terminals need to be isolated, use centralized forwarding. Otherwise, use distributed forwarding to improve bandwidth forwarding efficiency.
Precautions for configuring wired access terminal authentication
- It is not recommended to configure the combination of MAC and 802.1X (or Portal) authentication modes. If such combination is configured, concurrent access performance is reduced for terminals requiring 802.1X authentication when the system first performs MAC authentication on these terminals.
- When Portal authentication is configured, the built-in Portal server is not supported.
- Terminals cannot send DHCPv6 and neighbor discovery (ND) packets to trigger authentication.
- When authentication-free rules are configured on the parent, the parent delivers the authentication-free rules within the specified range to all ASs. For example, the parent can deliver authentication-free rules 0 to 127 to ASs of the S5720-EI model and 0 to 31 to ASs of other switch models. Authentication-free rules delivered to ASs do not carry interface information.
- In an SVF system, network access rights can be authorized through authentication-free rules but not a UCL group before users pass NAC authentication.
- Precautions for authorizing wired access terminals
- In an SVF system running a version earlier than V200R011C10, authorization VLANs cannot be assigned to wired users. In an SVF system running V200R011C10 or later, authorization VLANs can be assigned to wired users.
- Wired access terminal authentication mode
- Wireless access terminal authentication scenario
- Wireless access terminal authentication mode
Table 3 Recommended authentication modes in a wireless access terminal authentication scenario Scenario
Scenario Characteristics
Typical Terminal
Recommended Authentication Mode
Remarks
Campus Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) network
- The network is closed, users seldom change their locations, and high security is required.
- Many users roam simultaneously.
Laptops, PADs, and mobile phones
802.1X
- When a large number of users roam simultaneously, non-roaming users will not be disconnected, but roaming users may be disconnected.
- Roaming users will not be disconnected when a few users roam simultaneously.
- Use tunnel forwarding.
Educational institution
- The network is closed, and terminals are densely distributed.
- Many users roam simultaneously.
Laptops
MAC+Portal
- When a large number of users roam simultaneously, non-roaming users will not be disconnected, but roaming users may be disconnected.
- Use tunnel forwarding.
Precautions for configuring wireless access terminal authentication
You are advised to configure tunnel forwarding.
- Wireless access terminal authentication mode