STA Identification
Context
With the development of Internet, many enterprises allow employees to wirelessly access the enterprise intranet using their own intelligent devices such as cellphones, tablets, and laptops, which satisfies employees' pursuit of new technology and desire of being unique, and improves their efficiency as well. This is called Bring Your Own Device (BYOD). However, access to enterprise intranet through PCs may cause potential security risks, and traditional security technology based on user identity authentication and authorization can no longer guarantee network security. It is in such a background that the terminal type identification technology comes out. With this technology, the types of the devices that employees use to access the intranet can be identified, facilitating access control. During the implementation of BYOD, administrators can limit intranet access rights to specified types of mobile devices and perform authentication and authorization based on users, device types, access time, access points, and environment information about the devices.
A terminal type identification profile is configured with terminal types that can be identified by devices, and identification rules. With the configured identification rules, the types of devices using which employees access the intranet can be identified, helping administrators to control employees' access rights.

Only the S5720-HI, S5730-HI, S5731-H, S5731S-H, S5732-H, S6730-H, S6730S-H, and S6720-HI support STA identification.
This node is only available in the NAC unified and non-NETCONF modes.
Procedure
- Create a terminal identification profile.
- Create a preset terminal identification profile.
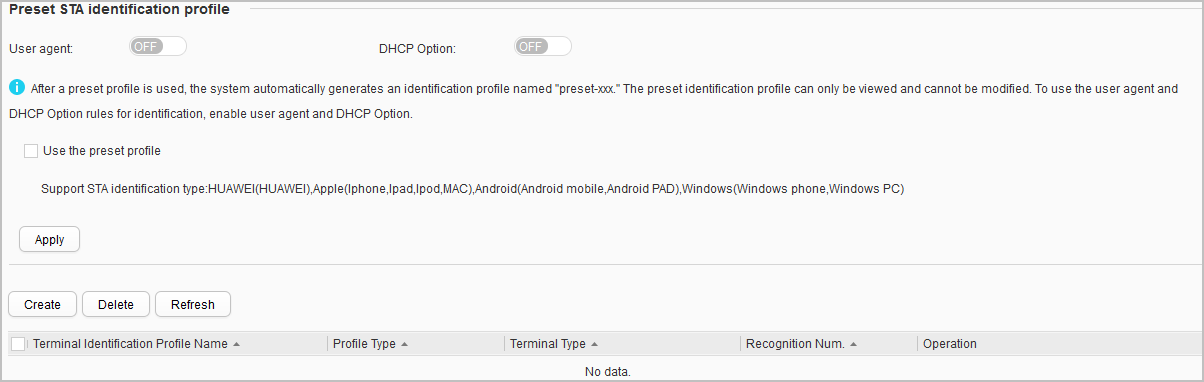
- Choose . The terminal identification page is displayed, as shown in Figure 1.
- Select Use the preset profile and click Apply to complete the configuration.

To use the user agent and DHCP Option rules for identification, enable user agent and DHCP Option.
- Create a user-defined terminal identification profile.
- Choose . The terminal identification page is displayed, as shown in Figure 1.
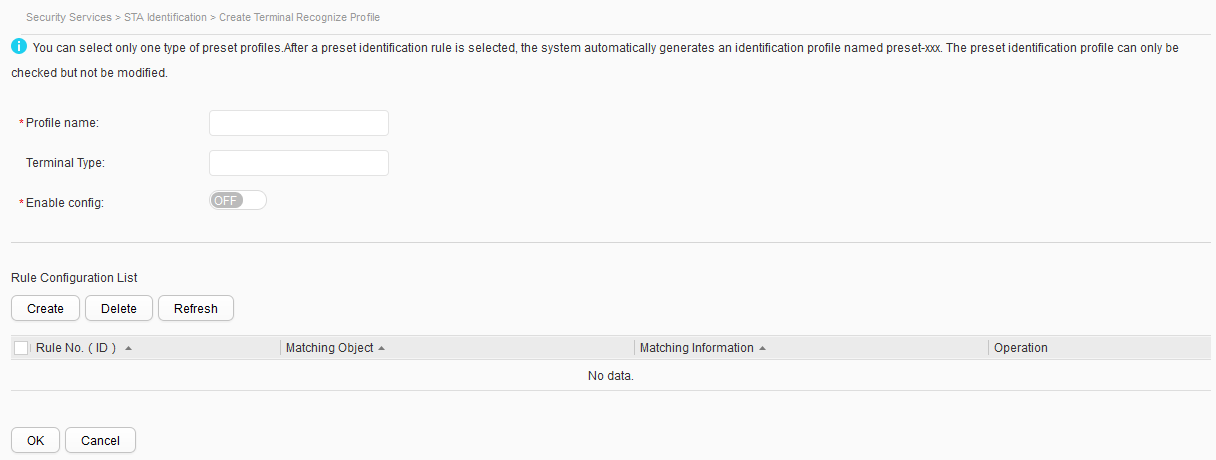
- Click Create. The page for creating a terminal identification profile is displayed, as shown in Figure 2.
Table 1 describes parameters on the page.
Table 1 Creating a terminal identification profile Item
Description
Profile name
Indicates the name of the new terminal identification profile, which cannot be modified.
Terminal Type
Indicates the terminal type ID. This parameter cannot be modified in the preset profile.
Enable config
Enables or disables terminal type identification.
NOTE:The prerequisite for enabling the terminal type identification function is that the terminal type ID has been configured.
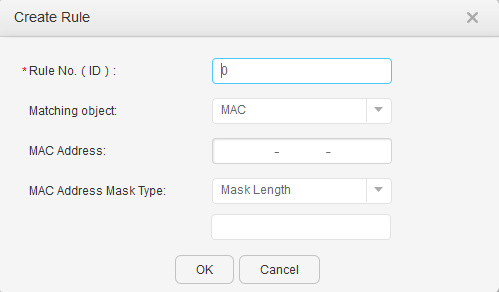
- Click Create in Rule Configuration List. The page for creating a rule is displayed, as shown in Figure 3.
Table 2 describes parameters on the page.
Table 2 Creating a rule Item
Description
Rule No. (ID)
Indicates the ID of an identification rule. This parameter cannot be modified.
Matching object
Indicates the rule for identifying a terminal type, including the MAC address, user agent, and DHCP option.- MAC: Match the first 12 bits of a terminal's MAC address, which is known as the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI), to identify the corresponding manufacturer.
- User Agent: Use the UA information carried in HTTP packets from a terminal to identify the operating system and its version, the CPU type, browser type, and browser version.
- DHCP option: Use the manufacturer information carried in Option12, Option55, and Option60 in DHCP packets from a terminal to identify the terminal's host name and manufacturer type.
MAC Address
Indicates the MAC address that a terminal must match.
This parameter is supported only when Matching object is set to MAC.
MAC Address Mask Type
Indicates the mask or mask length of a terminal's MAC address.
This parameter is supported only when Matching object is set to MAC.
UA information to be matched
Specifies the UA information that a terminal must match.
This parameter is supported only when Matching object is set to User Agent.
DHCP option
Indicates the DHCP option that a terminal must match.
This parameter is supported only when Matching object is set to DHCP option.
Option to be matched
Indicates partial match. The UA or Option information detected by the AC must be the same as or contain the value of option-text or user-agent-text.
This parameter is supported only when Matching object is set to DHCP option.
Matching character string format
Indicates the Option information that a terminal must match as an ASCII or hexadecimal string.
This parameter is supported only when Matching object is set to DHCP option.
Matching mode
Indicates exact match or partial match.- Exact: The UA or Option information detected by the AC must be the same as the value of option-text or user-agent-text.
- Partial: The UA or Option information detected by the AC must be the same as or contain the value of option-text or user-agent-text.
This parameter is supported only when Matching object is set to User Agent or DHCP option.
- Set the parameters.
In Rule No. (ID), select --, and or or to configure the matching mode for terminal type identification.
Click
 and
and  to change the matching order of rules.
to change the matching order of rules. - Click OK.
- Create a preset terminal identification profile.
- Modify a terminal identification profile.
- Restore a preset terminal identification profile.
- Choose . The terminal identification page is displayed, as shown in Figure 1.
- Click Recover preset next to the preset terminal identification profile to be restored. The modified preset terminal identification profile is restored to the default configuration.
- Delete a terminal identification profile.
- Choose . The terminal identification page is displayed, as shown in Figure 1.
- Select the terminal identification profile to be deleted, and click Delete.
- Click OK.