Understanding the Shopping Mall and Supermarket IoT Solution - Indoor Navigation
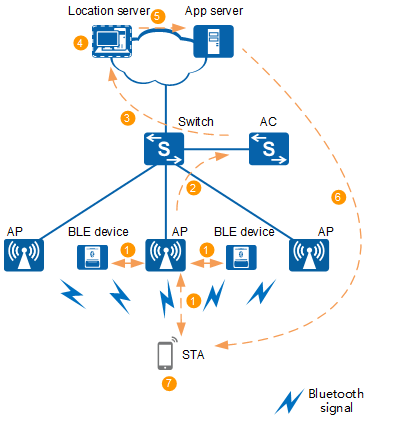
Figure 1 shows implementation of the intelligent indoor navigation solution.
The built-in Bluetooth module of an AP scans for Bluetooth broadcast frames in the surrounding environment to obtain the universal unique identifiers (UUIDs) and RSSI calibration values of surrounding BLE devices and Bluetooth terminals (mobile phones and tablets with the Bluetooth function enabled). The AP sends requests to the BLE devices and Bluetooth terminals to obtain BLE power information.
The AP reports obtained information such as UUIDs, RSSI calibration values, and BLE power of BLE devices to the AC, and reports Bluetooth terminal location packets to the AC or location server.
The Bluetooth broadcast function needs to be enabled for the built-in Bluetooth module of the AP, so that the AP can function as a BLE device to send BLE broadcast frames. In this case, the AP can directly report the UUID, RSSI calibration value, and power of the built-in Bluetooth module to the AC without the need of scanning.
The AC reports Bluetooth terminal location packets, as well as low power alarm and fault alarm information about BLE devices to the location server.
On the location server, make floor plans and location map models, add BLE devices, set their deployment locations, monitor their status, and compute Bluetooth terminal locations.
The app server obtains map information and BLE device location information from the location server.
The app server sends map information and BLE device locations to Bluetooth terminals.
Bluetooth terminals must be able to access the Internet through a WLAN or cellular network, so the indoor navigation app installed on the Bluetooth terminals can communicate with the app server.
- Enable the indoor navigation app on a Bluetooth terminal and perform the following steps:
Collect information about scanned BLE devices and their signal strengths.
Collect information about sensors of mobile phones, such as speed sensors and gyroscopes.
Obtain map information from the location server.
The Bluetooth terminal computes the location information and uses the computing results for applications such as indoor navigation, card seeking, and shop seeking to provide users with the navigation and car or shop seeking services.