Understanding the Smart Retail IoT Solution - ESL
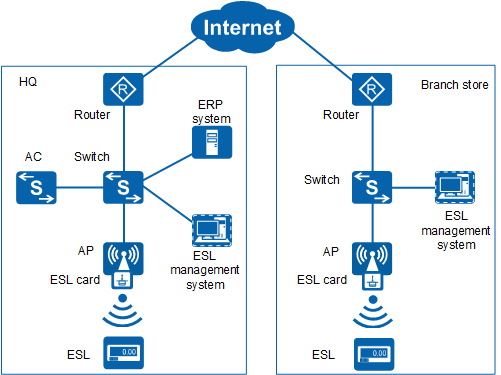
As shown in Figure 1, in the ESL solution, an ERP system is deployed at the headquarters of a company, while ESLs, ESL cards, and ESL management systems are deployed at both the headquarters and branch store. The ESL management systems at the headquarters and branch store are connected to the ERP system. When commodity prices are adjusted in the ERP system, price adjustment results are synchronized to the ESL management systems. The ESL management systems adjust commodity prices based on the price adjustment results in the ERP system and pre-configured price adjustment plan. In addition, the ESL management systems display other information about commodities on ESLs, such as the validity period, promotion description, and specifications.
The ESL solution is implemented in two phases.
Phase 1
In phase 1, ESL cards are initialized, ESLs are registered with the ESL management system, and ESL IDs are associated with commodity codes.
- The ESL management system is directly connected to ESL cards at Layer 2, and sends broadcast requests. After receiving the broadcast requests, ESL cards reply with their own IDs.
- After the ESL management system receives the ESL card IDs, the administrator configures IP addresses for the ESL cards on the GUI of the ESL management system.
- The ESL management system then assigns the IP addresses to the ESL cards for initialization.
- ESLs proactively send registration requests to ESL cards. The ESL cards receive and send the registration requests to the ESL management system.
After receiving the registration requests, the ESL management system allows the ESLs to register.
After the ESLs are registered, the ESL management system learns the ESL IDs and the IDs of the ESL cards that manage the ESLs. In this way, after the ESL IDs are associated with commodity codes, the ESL management system can deliver ESL update tasks to correct ESLs.
Use a handheld scanner to scan ESL IDs and commodity codes for association, or manually associate them in the ESL management system.
Phase 2
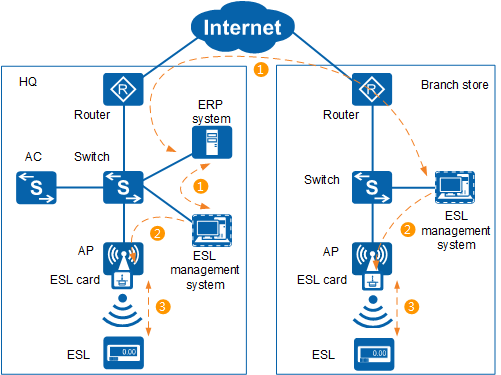
- The ERP system at the headquarters is used to maintain and update commodity price information. The ESL management system at the branch store sends data update requests to the ERP system, and obtains updated commodity information such as the commodity code and price.
- After obtaining updated information, the ESL management system delivers ESL update tasks to ESL cards as planned. ESL cards cache task data and wait for ESLs to initiate ESL update requests.
To save energy and prolong the service life of batteries, ESLs' radio modules are activated periodically. Within the activation period, ESLs proactively send requests to ESL cards to query whether ESL update tasks are available. If so, the ESLs obtain data and update information to be displayed. If not, the ESLs' radio modules keep their sleeping state until the next activation period.
In the current ESL solution, ESLs and ESL cards exchange packets with each other using 2.4 GHz radio frequency identification (RFID) technology.
- In most cases, ESL information is updated in non-business hours to prevent ESL information update from affecting normal business and avoid customer complaints.
- ESL information update during business hours rarely happens. Such scenario may exist only in small stores with only tens of ESLs and a small service data volume, such as bakeries. ESL information update takes a short time, so the interference time is short.