lacp force-forward
Function
The lacp force-forward command configures an Eth-Trunk member interface in Up state to forward data packets when the remote interface does not join the Eth-Trunk.
The undo lacp force-forward command restores the default setting.
By default, an Eth-Trunk member interface in Up state cannot forward data packets when the remote interface does not join the Eth-Trunk.
Usage Guidelines
Usage Scenario
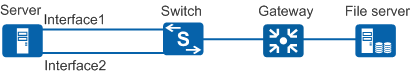
In Figure 1, two interfaces of two network
adapters on a server are directly connected to a switch. The switch
is configured with an Eth-Trunk in LACP mode. The process on the server
is as follows:
- The server configures an IP address for Interface1 based the default configuration during startup, and sends a request to the remote file server through Interface1 and downloads the configuration file from the remote file server.
- After the configuration file is downloaded successfully, the server aggregates two interfaces according to the configuration file. The server uses the two interfaces as Eth-Trunk member interfaces to perform LACP negotiation with the switch.
To address this issue, run the lacp force-forward command on the Eth-Trunk of the switch. The Eth-Trunk member interface in Up state can still forward data packets even though the remote device is not enabled with LACP.
Prerequisites
The Eth-Trunk has been configured to work in LACP mode by using the mode lacp command.
Precautions
- When this command is used, Layer 3 forwarding is not supported but the member interface in ForceFwd state can forward Layer 2 traffic. The ForceFwd state is automatically set when LACP negotiation fails, and cannot be changed manually. You can use the display eth-trunk command to check the value of the Status field.
- This command applies to only the scenario where an Eth-Trunk joins a VLAN as an access, hybrid, trunk, and dot1q-tunnel interfaces.
- When a spanning tree protocol (for example, STP, RSTP, or MSTP) is used, the member interface in ForceFwd state cannot be blocked. That is, the member interface in ForceFwd state can continue to forward data packets. When other loop prevention protocols such as ERPS and RRPP are used, the member interface in ForceFwd state can be blocked. The blocked member interface in ForceFwd state cannot forward data packets.
- This command cannot be used with E-Trunk. That is, this command cannot be used on the Eth-Trunk that joins an E-Trunk.
- This command cannot be used with max active-linknumber or least active-linknumber.