1588v2 takes effect after you configure 1588v2 in both the system and interface views. After 1588v2 is enabled in the system view, you also need to set other basic information, including the domain number and virtual clock ID, to establish a 1588v2 network.
Context
Determine 1588v2 device types based on the 1588v2 network plan before enabling 1588v2 in the system view on each
router. The following 1588v2 parameters can be set:
1588v2 clock type:
- OC: ordinary clock
- BC: boundary clock
- E2ETC: end-to-end transparent clock
- P2PTC: peer-to-peer transparent clock
- TCandBC: transparent and boundary clock
- E2ETCOC: end-to-end transparent clock and ordinary clock
- P2PTCOC: peer-to-peer transparent and ordinary clock
Clock domain number
A 1588v2 network
is large scale and allows multiple carriers to lease the 1588v2 network
as a bearer network. To transparently transmit 1588v2 packets for
specific carriers, the 1588v2 network can be logically divided into
clock domains. Each clock domain has a single clock source, and all
devices in the domain synchronize clock signals with the clock source.
Virtual clock ID
Uniquely identifies a 1588v2 router. A virtual clock ID remains even if the IPU is removed from a 1588v2 router.
Slave-only mode for an OC
An OC has only a
single 1588v2 interface. This means that the OC can function as the
master clock to advertise clock signals or as a slave clock to receive
upstream clock signals. To enable an OC to work only as a slave clock
on a clock synchronous network, run the ptp slaveonly command.
Automatic asymmetry measurement on BCs and TCandBCs over the 1588v2 ring network
Figure 1 Automatic asymmetry measurement over a 1588v2 ring network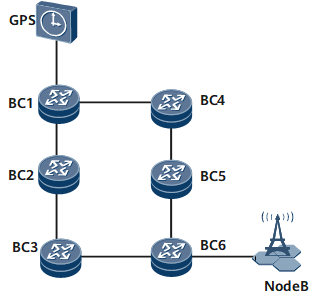
On the ring network shown in Figure 1, NodeB can synchronize clock signals with the global positioning system (GPS) only if fibers working in opposite directions on each network segment have the same length. Each node can synchronize clock signals with the GPS, irrespective of changes in clock sources that slave clocks trace. If a fiber between BC5 and BC6 is disconnected, BC6 traces clock signals of BC3. BC6 uses a compensation value that has calculated for the fiber between BC5 and BC6 to successfully synchronize clock signals with the GPS.
After the faulty fiber between BC5 and BC6 is repaired, the difference between the lengths of the fibers that transmit traffic in opposite directions changes, and BC6 traces clock signals of BC5, not BC3. BC6 uses the previous compensation value but fails to synchronize clock signals with the GPS. To address this problem, enable automatic asymmetry measurement on the NetEngine 8000 F.
Procedure
- Perform the following steps on each OC:
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run ptp enable
The 1588v2 function is enabled on the device.
If the device hardware supports ultra-high-precision timestamping, you can run the ptp uhpc enable command to improve the precision of time synchronization. To view the capabilities supported by the corresponding interface, run the display ptp interface { interface-name | interface-type interface-number } command.
- Run ptp device-type oc
The device type is set to OC.
- (Optional) Run ptp slaveonly
The OC is configured to work in slave-only mode.
The OC can be configured to work in slave-only mode before the OC synchronizes time signals with other clocks. The OC working in slave-only mode has its interfaces in Slave state. This means that the OC can function as a slave clock to receive clock signals from other clocks, but cannot function as a master clock to provide clock signals for other clocks.
- Run ptp domain domain-value
A clock domain number is specified.

Clocks in the same clock domain can exchange 1588v2 packets to synchronize time signals.
- (Optional) Run ptp source-switch ptsf enable
The PTSF-triggered source tracing function is enabled.
After this function is enabled, if the current time source has an offset change of greater than 1.1 µs for three consecutive seconds or the signal fails due to the loss of Sync packets, the device automatically switches to another valid time source after the time source fault is rectified, run the ptp source-switch ptsf recover command in the interface view to restore the current time source. If you want to automatically restore the time source after a certain period of time, run the ptp ptsf auto-recovery-time command to configure the PTSF auto-recovery time. By default, the PTSF auto-recovery time is 0 minute, that is, the function is disabled.
- (Optional) Run ptp virtual-clock-id clock-id-value
A virtual clock ID is set.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
- Perform the following steps on each BC:
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run ptp enable
The 1588v2 function is enabled on the device.
If the device hardware supports ultra-high-precision timestamping, you can run the ptp uhpc enable command to improve the precision of time synchronization. To view the capabilities supported by the corresponding interface, run the display ptp interface { interface-name | interface-type interface-number } command.
- Run ptp device-type bc
The device type is set to BC.
- Run ptp domain domain-value
A clock domain number is specified.

Clocks in the same clock domain can exchange 1588v2 packets to synchronize time signals.
- (Optional) Run ptp source-switch ptsf enable
The PTSF-triggered source tracing function is enabled.
After this function is enabled, if the current time source has an offset change of greater than 1.1 µs for three consecutive seconds or the signal fails due to the loss of Sync packets, the device automatically switches to another valid time source after the time source fault is rectified, run the ptp source-switch ptsf recover command in the interface view to restore the current time source. If you want to automatically restore the time source after a certain period of time, run the ptp ptsf auto-recovery-time command to configure the PTSF auto-recovery time
- (Optional) Run ptp virtual-clock-id clock-id-value
A virtual clock ID is set.
- (Optional) Run ptp asymmetry-measure enable
Automatic asymmetry measurement is enabled on the router over a 1588v2 ring network.
- (Optional) Run ptp max-steps-removedmax-steps-removed-value
The maximum number of hops for time synchronization is configured.
A clock source is considered unavailable if stepsRemoved in the Announce packets received by the clock source is greater than or equal to max-steps-removed-value.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
- Perform the following steps on each TC and TCOC:
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run ptp enable
The 1588v2 function is enabled on the device.
If the device hardware supports ultra-high-precision timestamping, you can run the ptp uhpc enable command to improve the precision of time synchronization. To view the capabilities supported by the corresponding interface, run the display ptp interface { interface-name | interface-type interface-number } command.
- Run ptp device-type { e2etc | e2etcoc | p2ptc | p2ptcoc }
The device type is set to TC or TCOC. One of the following parameters can be configured:
- e2etc: The device type is set to E2ETC.
- e2etcoc: The device type is set to E2ETCOC.
- p2ptc: The device type is set to P2PTC.
- p2ptcoc: The device type is set to P2PTCOC.

A TCOC has the same functions as a TC and also implements frequency synchronization.
- Run ptp domain domain-value
A clock domain number is specified.

Clocks in the same clock domain can exchange 1588v2 packets to synchronize time signals.
- (Optional) Run ptp source-switch ptsf enable The PTSF-triggered source tracing function is enabled.
After this function is enabled, if the current time source has an offset change of greater than 1.1 µs for three consecutive seconds or the signal fails due to the loss of Sync packets, the device automatically switches to another valid time source After the time source fault is rectified, run the ptp source-switch ptsf recover command in the interface view to restore the current time source. If you want to automatically restore the time source after a certain period of time, run the ptp ptsf auto-recovery-time command to configure the PTSF auto-recovery time
- (Optional) Run ptp virtual-clock-id clock-id-value
A virtual clock ID is set.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
- Perform the following steps on each TCandBC:
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run ptp enable
The 1588v2 function is enabled on the device.
If the device hardware supports ultra-high-precision timestamping, you can run the ptp uhpc enable command to improve the precision of time synchronization. To view the capabilities supported by the corresponding interface, run the display ptp interface { interface-name | interface-type interface-number } command.
- Run ptp device-type tcandbc
The device type is set to TCandBC.
- Run ptp domain domain-value
A clock domain number is specified.

Clocks in the same clock domain can exchange 1588v2 packets to synchronize time signals.
- (Optional) Run ptp source-switch ptsf enable
The PTSF-triggered source tracing function is enabled.
After this function is enabled, if the current time source has an offset change of greater than 1.1 µs for three consecutive seconds or the signal fails due to the loss of Sync packets, the device automatically switches to another valid time source After the time source fault is rectified, run the ptp source-switch ptsf recover command in the interface view to restore the current time source. If you want to automatically restore the time source after a certain period of time, run the ptp ptsf auto-recovery-time command to configure the PTSF auto-recovery time
- (Optional) Run ptp virtual-clock-id clock-id-value
A virtual clock ID is set.
- (Optional) Run ptp asymmetry-measure enable
Automatic asymmetry measurement is enabled on the router over a 1588v2 ring network.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.

