Overview
PTP Clock Types Supported by the NetEngine 8000 F
CU-106 supports the following types of PTP clocks:
- Telecom grandmaster (T-GM): is a master-only clock that can have one or more PTP ports. It does not trace other PTP clocks.
- Telecom boundary clock (T-BC): can be either a master clock or a clock tracing another PTP clock.
- Telecom transparent clock (T-TC): forwards CU-106 packets. T-TCs correct the forwarding delay in CU-106 packets, instead of synchronizing time with any port.
- Telecom time slave clock (T-TSC): is a slave-only clock and cannot be used as a master clock.
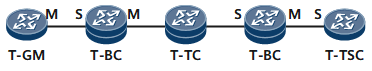
Figure 1 shows the positions of the T-GM, T-BC, T-TC, and T-TSC on a time synchronization network.
Delay Measurement Mechanism Supported by the NetEngine 8000 F
The NetEngine 8000 F supports the delay request-response mechanism. Specifically, the system calculates the time offset according to the link delay between the master and slave clocks.
Clock Source Tracing Modes Supported by the NetEngine 8000 F
BMCA
On a CU-106 network, all clocks are deployed in a hierarchical structure according to the master-slave relationship. The grandmaster clock provides the reference time and is at the highest stratum level. Such a topology can be automatically generated through the best master clock algorithm (BMCA).