Example for Configuring ESQM End-to-End Performance Measurement
This section describes how to use ESQM to collect end-to-end packet loss and delay statistics on an L3VPN HoVPN with an L3EVPN.
Networking Requirements
As networks rapidly develop and applications become diversified, various value-added services are widely used. Link connectivity and network performance influence network quality. Therefore, performance monitoring is especially important for service transmission.
For example, users will not sense any change in voice quality if the packet loss rate on voice links is lower than 5%. However, if the packet loss rate is higher than 10%, user experience obviously degrades.
The real-time services such as Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), online gaming, and online video require the delay lower than 100 ms. Some delay-sensitive services even require that the delay be lower than 50 ms. Otherwise, user experience will degrade.
To meet high requirements for voice, online gaming, and online video on the network, carriers should be able to monitor the packet loss and delay of the links. They can adjust the links if service quality decreases.
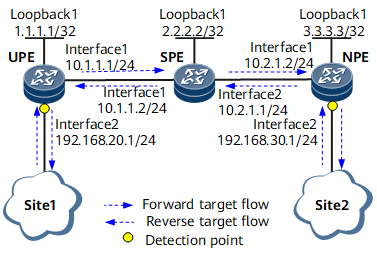
As shown in Figure 1, an access network is deployed between a UPE and an SPE, and an aggregation network is deployed between an SPE and an NPE. The forward service flow enters the network through the UPE, travels across the SPE, and leaves the network through the NPE. The backward service flow enters the network through the NPE, also travels across the SPE, and leaves the network through the UPE.
Device (Role) |
Interface Name |
Interface |
Peer Device (Role) |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|
UPE |
- |
Loopback1 |
- |
1.1.1.1/32 |
interface1 |
GE0/1/0 |
SPE |
10.1.1.1/24 |
|
interface2 |
GE0/1/8 |
Site1 |
192.168.20.1/24 |
|
SPE |
- |
Loopback1 |
- |
2.2.2.2/32 |
interface1 |
GE0/1/0 |
UPE |
10.1.1.2/24 |
|
interface2 |
GE0/1/8 |
NPE |
10.2.1.1/24 |
|
NPE |
- |
Loopback1 |
- |
3.3.3.3/32 |
interface1 |
GE0/1/0 |
SPE |
10.2.1.2/24 |
|
interface2 |
GE0/1/8 |
Site2 |
192.168.30.1/24 |
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Deploy IGPs between the UPE and SPE and between the SPE and NPE. In this example, OSPF runs between the UPE and SPE, and IS-IS runs between the SPE and NPE.
Configure MPLS LDP on the UPE, SPE, and NPE.
Configure VPN instances on the UPE, SPE, and NPE.
Bind the access-side interfaces on the UPE and NPE to the VPN instances.
Configure VPN static default routes on the SPE.
Configure a route-policy on the NPE to disable the NPE from receiving the default routes.
Configure BGP EVPN on the SPE and NPE.
Configure a BGP-VPNv4 peer relationship between the UPE and SPE, specify the UPE as the lower-level PE of the SPE, and configure the SPE to import default VPN routes.
Configure route regeneration on the SPE.
- Configure packet loss and delay measurement on the link between the UPE and NPE to monitor the link status in an end-to-end manner.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
- IP address of each interface listed in Table 1
- OSPF and IS-IS as IGP protocols
MPLS LSR IDs of UPE (1.1.1.1), SPE (2.2.2.2), and NPE (3.3.3.3)
VPN instance name vpn1 and RD 100:1
VPN targets 1:1 (import and export) of vpn1 and 2:2 for EVPN
- Measurement interval 10s for the ESQM instance
- Target flow's source IP address (192.168.20.2) and destination IP address (192.168.30.2)
Procedure
Configure an L3VPN HoVPN with an L3EVPN on the UPE, SPE, and NPE. For configuration details, see Configuration Files.
Configure ESQM measurement on the UPE and NPE, and inject unidirectional traffic from the UPE to the NPE.
# Configure inbound ESQM on the user side of the UPE.
<UPE> system-view [~UPE] esqm [*UPE-esqm] commit [~UPE-esqm] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 [~UPE—GigabitEthernet0/1/8] esqm service-stream inbound [*UPE—GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit
# Configure inbound ESQM on the user side of the NPE.
<NPE> system-view [~NPE] esqm [*NPE-esqm] commit [~NPE-esqm] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [~NPE—GigabitEthernet0/1/0] esqm service-stream inbound [*NPE—GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit
Configuration Files
- UPE configuration file
# sysname UPE # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 2:2 export-extcommunity evpn vpn-target 2:2 import-extcommunity evpn evpn mpls routing-enable # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 esqm service-stream inbound # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 import-route direct advertise l2vpn evpn # l2vpn-family evpn undo policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # esqm # return
- SPE configuration file
# sysname SPE # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 2:2 export-extcommunity evpn vpn-target 2:2 import-extcommunity evpn evpn mpls routing-enable # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls # mpls ldp # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.1 enable peer 3.3.3.3 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 network 0.0.0.0 advertise l2vpn evpn # l2vpn-family evpn undo policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable peer 1.1.1.1 upe peer 1.1.1.1 import reoriginate peer 3.3.3.3 enable peer 3.3.3.3 advertise route-reoriginated evpn ip # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # ip route-static vpn-instance vpn1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 NULL0 # return
- NPE configuration file
# sysname NPE # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance import route-policy SPE evpn vpn-target 2:2 export-extcommunity evpn vpn-target 2:2 import-extcommunity evpn evpn mpls routing-enable # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # mpls # mpls ldp # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp esqm service-stream inbound # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 import-route direct advertise l2vpn evpn # l2vpn-family evpn undo policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.2 enable # route-policy SPE deny node 10 if-match ip-prefix default # route-policy SPE permit node 20 # ip ip-prefix default index 10 permit 0.0.0.0 0 # esqm # return