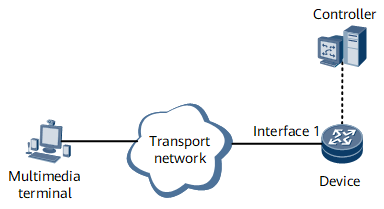
Understanding Flow Recognition
Flow recognition enables a device to collect the septuple information (source and destination MAC addresses, source and destination IP addresses, source and destination port numbers, and protocol type) of the upstream traffic on an interface, and identifies a flow based on the information. The device then sends the flow's statistics (such as the numbers of packets and bytes, timestamps, and interface information) to a controller for display and traffic identification.
Implementation
To calculate the flow rate, the controller needs to receive the data information of each flow. Table 1 describes the flow data fields collected and sent by the device to the controller.
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
srcMac |
Character string |
Source MAC address |
dstMac |
Character string |
Destination MAC address |
srcIpAddr |
Character string |
Source IP address |
dstIpAddr |
Character string |
Destination IP address |
srcPort |
Integer (2 bytes) |
Source port number |
dstPort |
Integer (2 bytes) |
Destination port number |
protocol |
Integer (1 byte) |
Protocol type |
direction |
Integer (1 byte) |
Direction in which the traffic enters the interface:
|
ifName |
Character string |
Interface name |
timeStampSec |
Integer (4 bytes) |
Timestamp in seconds, which is used to calculate a time difference |
timeStampNsec |
Integer (4 bytes) |
Timestamp in nanoseconds, which is used to calculate a time difference |
packetNum |
Integer (8 bytes) |
Number of packets |
bytesNum |
Integer (8 bytes) |
Number of bytes of a packet |
If the device consecutively collects statistics about a flow twice, the flow's rate is calculated as follows:
- Number of packets forwarded per second = (packetNum2 - packetNum1)/(timeStampSec2 - timeStampSec1)
- Number of bytes forwarded per second = (bytesNum2 - bytesNum1)/(timeStampSec2 - timeStampSec1)