Basic Principles of eMDI Detection
eMDI detection can be deployed through the NMS or using commands on devices. eMDI detection can be deployed on all nodes from the UPE to the CR (UPE and CR included). eMDI detection supports the single-node, two-node, and multi-node deployment modes.
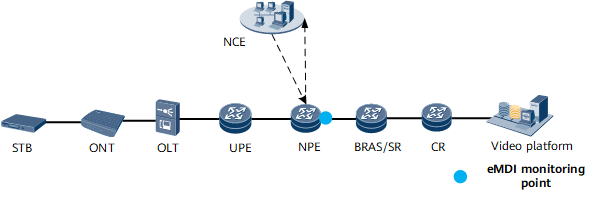
- Single-node deployment: The eMDI detection solution is deployed only on one node to demarcate faults between upstream and downstream network segments, as shown in Figure 1.
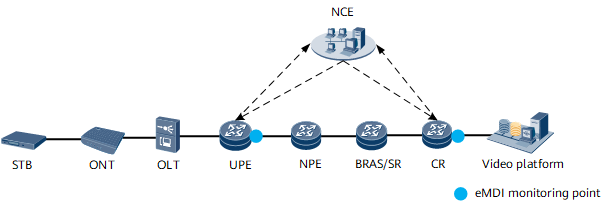
- Two-node deployment: The eMDI detection solution can be deployed on the UPE and CR to demarcate faults on three network segments: user access, transmission network, and video source, as shown in Figure 2.
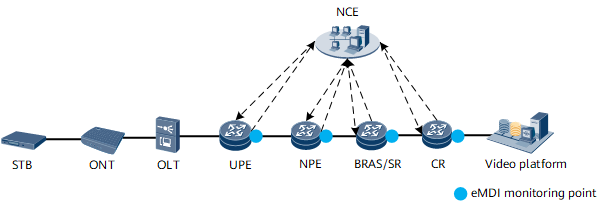
- Multi-node deployment: The eMDI detection solution can be deployed on UPE, NPE, BRAS/SR, and CR nodes to achieve fault demarcation with higher precision, as shown in Figure 3.
Deploying more eMDI monitoring points leads to higher precision of fault demarcation.
Detection Principles
The eMDI detection solution is a distributed board detection solution. During solution deployment, the channels to be detected are added to a channel group, the eMDI-capable boards are added to a board group, and the channel group is bound to the board group. With detection on the board NP, the video streams of specified channels can be detected in distributed mode.
This solution supports detection only of UDP-based Real-Time Transport Report (RTP) video streams. The NP of the board to be detected performs validity check and RTP check on the IP header, UDP header, and RTP header of RTP packets and calculates the packet loss rate and packet disorder rate based on the sequence number in the RTP header. Then, the NP calculates jitter based on the timestamp in the RTP header, achieving real-time monitoring of video quality.
- The NMS delivers eMDI monitoring instructions to a device.
- The device monitors eMDI indicators in real time.
- The device periodically reports the monitored eMDI indicators and alarms to the NMS.
- The NMS displays eMDI indicators in GUI mode and supports analysis on fault demarcation and locating.
Indicator Collection
eMDI can obtain monitoring data from a device on a regular basis and periodically send the data to the NMS in various modes such as telemetry. After analysis on the NMS, the monitoring data can be displayed in various forms, such as a trend chart.
eMDI also supports reporting of alarms to the NMS. The alarm thresholds and the number of alarm suppressions can be configured as required.
Fault Demarcation Principles
When a fault is detected using eMDI on a node on an IP network, the detection data on multiple nodes can be compared to demarcate the faulty network segment. As shown in Figure 3, if a fault is detected on the NPE but not on the SR, it can be determined that the fault occurs on the SR or the network segment between the NPE and SR.