Understanding sFlow
Architecture of an sFlow System
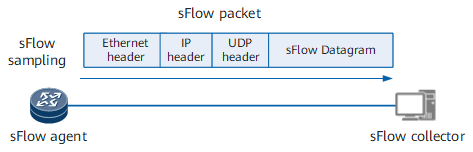
As shown in Figure 1, the sFlow system involves an sFlow agent embedded in a device and a remote sFlow collector. The sFlow agent obtains traffic statistics from an interface using sampling and encapsulates the statistics into sFlow packets. When an sFlow packet buffer overflows or an sFlow packet expires (expiry period of 1 second), the agent sends the sFlow packets to the collector. The collector analyzes these sFlow packets and displays traffic statistics in a report.

An sFlow agent is usually deployed on a network device. This section describes its implementation.
An sFlow collector is a PC or server that receives sFlow packets from an sFlow agent. The client software, for example, sFlow Trend, must be installed on an sFlow collector to analyze sFlow packets. To obtain the sFlow Trend client and download the usage guide, visit www.sflow.org.
sFlow Packet Format
- Flow sample
- Expanded Flow sample
- Counter sample
- Expanded Counter sample

Currently, devices support only sFlow version 5.
sFlow Sampling
An sFlow agent provides flow sampling and counter sampling.

Currently, devices support only flow sampling.
Flow sampling
With flow sampling, an agent samples ingress packets, egress packets, or both on an interface based on a sampling rate, and parses the packets to obtain information about packet data content. Table 1 describes the main fields in flow sampling packets. Data in these fields is encapsulated into an sFlow packet and then sent to a collector. Flow sampling focuses on traffic attributes to monitor and parse traffic behaviors on the network. Flow sampling samples packets on an interface, and currently supports only random sampling. In random sampling mode, every N packets are sampled randomly.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Raw Packet Header |
Records the entire packet or part of the packet header. |
Ethernet Frame Data |
Analyzes Ethernet headers in Ethernet frames. |
IPv4 Data |
Analyzes IPv4 headers in IPv4 packets. |
IPv6 Data |
Analyzes IPv6 headers in IPv6 packets. |
Extended Switch Data |
Records VLAN translation and 802.1Q priority mapping information in Ethernet frames. VLAN ID 0 indicates an invalid VLAN. |
Extended Router Data |
Records routing information for packets. |
Extended Gateway Data |
Records BGP routing information for packets. |
Counter sampling
With counter sampling, an agent periodically obtains traffic statistics on an interface. Table 2 describes the main fields in counter sampling packets. Compared with flow sampling, counter sampling focuses on traffic statistics on an interface rather than traffic attributes.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Generic Interface Counters |
Records basic information and traffic statistics on an interface. |
Ethernet Interface Counters |
Records traffic statistics on an Ethernet interface. |
Processor Information |
Records CPU usage and memory usage of a device. |
Flow sampling and counter sampling are independent of each other. Flow sampling obtains information about flows of a specified service, whereas counter sampling obtains traffic statistics on an interface. You can configure either or both sampling modes.