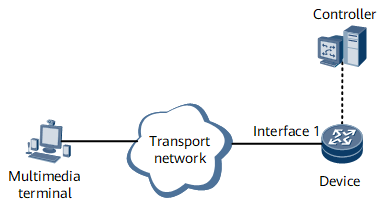
Overview of Flow Recognition
Flow recognition enables a device to collect the septuple information (source and destination MAC addresses, source and destination IP addresses, source and destination port numbers, and protocol type) of the upstream traffic on an interface, and identifies a flow based on the information. The device then sends the flow's statistics (such as the numbers of packets and bytes, timestamps, and interface information) to a controller for display and traffic identification.
Background
In the radio and television industry, especially in TV stations or media centers, IP-based production and broadcasting networks are gaining in popularity. Related IP standards are being formulated, which is an important step in the development of the 4K industry. However, IP-based production and broadcasting networks require switching among multiple video sources or cameras during video production and live transmission to achieve the optimal video display effect. Currently, IP-based devices use IGMP to switch between different multicast groups. When IGMP starts or stops multicast forwarding, it does not determine the frame boundary of a video. As a result, the forwarded content is incomplete and the video is damaged (such as artifacts, jitters, black screens, and static frames).
The quintuple information (source and destination IP addresses, source and destination port numbers, and protocol type) may not distinguish between flows. To resolve this issue, configure flow recognition based on the septuple information (source and destination MAC addresses, source and destination IP addresses, source and destination port numbers, and protocol type) on a device. A controller calculates the flow rate based on the information reported by the device, and determines whether the flow is video or audio flow based on the flow rate. The device then replicates and broadcasts the identified flow quickly and accurately.
Flow recognition is used to identify video and audio flows on IP-based production and broadcasting networks.
Implementation
To calculate the flow rate, the controller needs to receive the data information of each flow. Table 1 describes the flow data fields collected and sent by the device to the controller.
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
srcMac |
Character string |
Source MAC address |
dstMac |
Character string |
Destination MAC address |
srcIpAddr |
Character string |
Source IP address. |
dstIpAddr |
Character string |
Destination IP address |
srcPort |
Integer (4 bytes) |
Source port number |
dstPort |
Integer (4 bytes) |
Destination port number |
protocol |
Integer (4 bytes) |
Protocol type |
direction |
Integer (4 bytes) |
Direction in which the traffic enters the interface:
|
ifName |
Integer (4 bytes) |
Interface name |
timeStampSec |
Integer (4 bytes) |
Timestamp in seconds, which is used to calculate a time difference |
timeStampNsec |
Integer (4 bytes) |
Timestamp in nanoseconds, which is used to calculate a time difference |
packetNum |
Integer (8 bytes) |
Number of packets |
bytesNum |
Integer (8 bytes) |
Number of bytes of a packet |
- Number of packets forwarded per second = (packetNum2 - packetNum1)/(timeStampSec2 - timeStampSec1)
- Number of bytes forwarded per second = (bytesNum2 - bytesNum1)/(timeStampSec2 - timeStampSec1)