Example for Configuring IPoEoVLAN Access
This section provides an example for configuring IPoEoVLAN access.
Networking Requirements
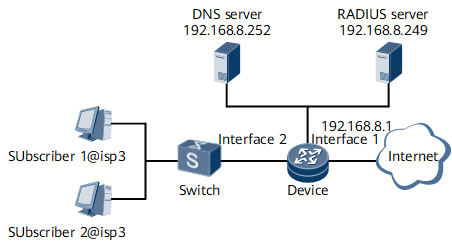
On the network shown in Figure 1, the networking requirements are as follows:
A user belongs to the domain isp3 and accesses the network through GE 0/1/2.1 on the device in IPoEoVLAN mode. The LAN switch tags user packets with VLAN 1 and VLAN 2.
The user adopts binding authentication, RADIUS authentication, and RADIUS accounting.
The IP address of the RADIUS server is 192.168.8.249. The authentication port number is 1812, and the accounting port number is 1813. The standard RADIUS protocol is adopted. The shared key is it-is-my-secret1.
The IP address of the DNS server is 192.168.8.252.
The network-side interface is GE 0/1/1.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure authentication and accounting schemes.
Configure a RADIUS server group.
Configure an address pool.
Configure an authentication domain.
Configure a BAS interface and an upstream interface.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Authentication template name and authentication mode
Accounting template name and accounting mode
RADIUS server group name, and IP addresses and port numbers of the RADIUS authentication server and accounting server
IP address pool, gateway address, and DNS server address
Domain name
BAS interface parameters
Procedure
- Configure AAA schemes.
# Configure an authentication scheme.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] aaa [*HUAWEI-aaa] authentication-scheme auth3 [*HUAWEI-aaa-authen-auth3] authentication-mode radius [*HUAWEI-aaa-authen-auth3] commit [~HUAWEI-aaa-authen-auth3] quit
# Configure an accounting scheme.
[~HUAWEI-aaa] accounting-scheme acct3 [*HUAWEI-aaa-accounting-acct3] accounting-mode radius [*HUAWEI-aaa-accounting-acct3] commit [~HUAWEI-aaa-accounting-acct3] quit [~HUAWEI-aaa] quit
- Configure a RADIUS server group.
[~HUAWEI] radius-server group rd3 [*HUAWEI-radius-rd3] radius-server authentication 192.168.8.249 1812 [*HUAWEI-radius-rd3] radius-server accounting 192.168.8.249 1813 [*HUAWEI-radius-rd3] commit [~HUAWEI-radius-rd3] radius-server type standard [*HUAWEI-radius-rd3] radius-server shared-key-cipher it-is-my-secret1 [*HUAWEI-radius-rd3] commit [~HUAWEI-radius-rd3] quit
- Configure an address pool.
[~HUAWEI] ip pool pool3 bas local [*HUAWEI-ip-pool-pool3] gateway 10.82.2.1 255.255.255.0 [*HUAWEI-ip-pool-pool3] commit [~HUAWEI-ip-pool-pool3] section 0 10.82.2.2 10.82.2.200 [~HUAWEI-ip-pool-pool3] dns-server 192.168.8.252 [*HUAWEI-ip-pool-pool3] commit [~HUAWEI-ip-pool-pool3] quit

The configured address pool is used for the authentication domain. The pre-authentication domain is not required because a user that adopts binding authentication can be authenticated automatically when the user goes online.
- Configure an authentication domain.
[~HUAWEI] aaa [~HUAWEI-aaa] domain isp3 [*HUAWEI-aaa-domain-isp3] authentication-scheme auth3 [*HUAWEI-aaa-domain-isp3] accounting-scheme acct3 [*HUAWEI-aaa-domain-isp3] radius-server group rd3 [*HUAWEI-aaa-domain-isp3] commit [~HUAWEI-aaa-domain-isp3] ip-pool pool3 [~HUAWEI-aaa-domain-isp3] quit [~HUAWEI-aaa] quit

When a user obtains an IP address in binding authentication, the device authenticates the user automatically. Therefore, you do not need to configure an ACL to control the network access permissions of the user before authentication. Instead, you need to configure an ACL to control the network access permissions of the user after authentication.
- Configure interfaces.
# Configure a BAS interface.
[~HUAWEI] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/2.1 [*HUAWEI-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] commit [~HUAWEI-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] user-vlan 1 2 [~HUAWEI-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1-vlan-1-2] quit [~HUAWEI-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] bas [~HUAWEI-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1-bas] access-type layer2-subscriber [*HUAWEI-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1-bas] authentication-method bind [*HUAWEI-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1-bas] default-domain authentication isp3 [*HUAWEI-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1-bas] commit [~HUAWEI-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1-bas] quit [~HUAWEI-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] quit

The user name for binding authentication is automatically generated based on the location where the user accesses the NetEngine 8000 F. Therefore, the user name on the RADIUS server must be configured according to the name generation rule. The password is vlan.
For details about the user name format used in binding authentication, see the description of the vlanpvc-to-username command in the HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F Series Router Command Reference.
# Configure an upstream interface.
[~HUAWEI] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [*HUAWEI-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 192.168.8.1 255.255.255.0 [*HUAWEI-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~HUAWEI-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
Configuration Files
# sysname HUAWEI # radius-server group rd3 radius-server shared-key-cipher %^%#vS%796FO7%C~pB%CR=q;j}gSCqR-X6+P!.DYI@)%^%# radius-server authentication 192.168.8.249 1812 weight 0 radius-server accounting 192.168.8.249 1813 weight 0 # ip pool pool3 bas local gateway 10.82.2.1 255.255.255.0 section 0 10.82.2.2 10.82.2.200 dns-server 192.168.8.252 # aaa # authentication-scheme auth3 # accounting-scheme acct3 # domain isp3 authentication-scheme auth3 accounting-scheme acct3 radius-server group rd3 ip-pool pool3 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 ip address 192.168.8.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1 user-vlan 1 2 bas # access-type layer2-subscriber default-domain authentication isp3 authentication-method bind # # return