Example for Configuring Distributed MAP-T
This section provides an example for configuring the distributed MAP-T function on the device that functions as the MAP-BR and BRAS.
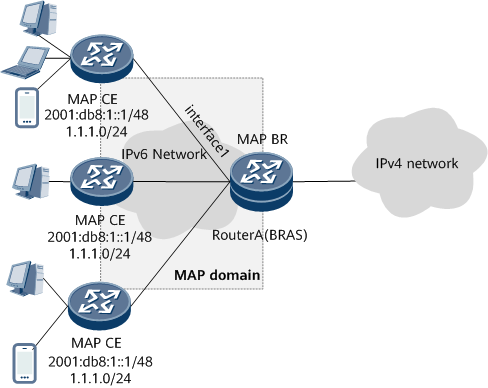
Networking Requirements
In a distributed scenario shown in Figure 1, both the MAP-BR and BRAS reside on Router A. The BRAS functions as a DHCPv6 server to deliver MAP addresses and mapping rules to MAP-CEs in DHCPv6 IA_PD mode. Router A also functions as a MAP-BR and resides on the edge of a MAP domain. Router A allows the MAP-CEs to access the public IPv4 network through the IPv6 network that is within the MAP domain. In addition, the MAP-CEs can use each other's public IPv4 address to communicate through the MAP-BR.
Prerequisites
The MAP license has been loaded to the MAP-BR, and the MAP function has been activated.
The MAP-BR has at least one interface board that supports the MAP function.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Configure BMR rules.
- Configure the prefix address and length of a DMR.
- Configure an IPv6 prefix pool and address pool.
- Configure a MAP-T instance and bind the DMR and BMR rules to the MAP-T instance.
- Configure user access.
Data Preparation
BMR name (bmr_name), IPv6 address (2001:db8:1::1), prefix length (48), IPv4 address (1.1.1.0), mask length (24), EA-length (16), and PSID-offset length (4)
DMR name (dmr_name), IPv6 address (2001:db8:3::1), and prefix length (96 bits)
MAP-T instance name (1) and ID (1)
Procedure
- Configure a BMR on the BRAS to instruct the BRAS to assign IPv6 and IPv4 addresses to the MAP-CEs. In this example, the IPv6 prefix address assigned to the MAP-CE is 2001:db8:1::1, the prefix length is 48, and the length of the EA-bits is 16. The public IPv4 prefix address allocated to the MAP-CE is 1.1.1.0 and the prefix length is 24. The offset length of the PSID field is 4, which means that ports 0 to 4096 are reserved.
<RouterA> system-view [~RouterA] map rule bmr_name [*RouterA-map-rule-bmr_name] rule-prefix 2001:db8:1::1 prefix-length 48 ipv4-prefix 1.1.1.0 prefix-length 24 ea-length 16 psid-offset 4 [*RouterA-map-rule-bmr_name] commit [~RouterA-map-rule-bmr_name] quit
- Configure a DMR rule on the device and combine the IPv6 prefix configured in the DMR rule with the destination IPv4 address on the MAP-CE to form a destination IPv6 address.
[~RouterA] dmr-prefix dmr_name ipv6-prefix 2001:db8:3::1 prefix-length 96 [*RouterA] commit
- Configure an IPv6 prefix pool and an address pool on the device.
- Configure an IPv6 prefix pool named pre1, bind it to the MAP rule named bmr_name, and assign IPv4 and IPv6 addresses that comply with BMR rules.
[~RouterA] ipv6 prefix pre1 delegation [*RouterA-ipv6-prefix-pre1] map-rule bmr_name [*RouterA-ipv6-prefix-pre1] commit [~RouterA-ipv6-prefix-pre1] quit
- Configure an IPv6 address pool named pool1 and bind it to the prefix pool named pre1. Bind the prefix dmr_name to the IPv6 address pool so that the BRAS encapsulates the IPv6 prefix as Option 91 information (OPTION_S46_DMR) into the DHCPv6 Response message sent to MAP-CEs.
[~RouterA] ipv6 pool pool1 bas delegation [*RouterA-ipv6-pool-pool1] prefix pre1 [*RouterA-ipv6-pool-pool1] option-s46 dmr-prefix dmr_name [*RouterA-ipv6-pool-pool1] commit [~RouterA-ipv6-pool-pool1] quit
- Configure an IPv6 prefix pool named pre1, bind it to the MAP rule named bmr_name, and assign IPv4 and IPv6 addresses that comply with BMR rules.
- Configure a MAP-T instance on the device and bind the configured DMR and BMR rules to the MAP-T instance. The DMR rule is used to translate the IPv6 packets imported from the MAP-CE to the MAP-T instance for address translation and bind the BMR rules to encapsulate and verify the packets in the instance.
[~RouterA] map-t instance 1 id 1 [*RouterA-map-t-instance-1] dmr-prefix dmr_name [*RouterA-map-t-instance-1] map-rule bmr_name [*RouterA-map-t-instance-1] commit [~RouterA-map-t-instance-1] quit
- Configure IP addresses of the user- and network-side interfaces on the MAP-BR.
[~RouterA] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 [~RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ipv6 enable [*RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ipv6 address auto link-local [*RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
- Configure a user access domain.
[~RouterA] aaa [*RouterA-aaa] domain map-t [*RouterA-aaa-map-t] authentication-scheme default0 [*RouterA-aaa-map-t] accounting-scheme default0 [*RouterA-aaa-map-t] commit [~RouterA-aaa-map-t] ipv6-pool pool1 [~RouterA-aaa-map-t] quit [~RouterA-aaa] quit
- Configure a DUID for the DHCPv6 server.
[~RouterA] dhcpv6 duid llt [*RouterA] commit
- Configure IPoEv6 access.
[~RouterA] interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 [*RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] bas [*RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8-bas] access-type layer2-subscriber default-domain authentication map-t [~RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8-bas] authentication-method-ipv6 bind [*RouterA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8-bas] commit
Router A Configuration File
#
dmr-prefix dmr_name ipv6-prefix 2001:db8:3::1 prefix-length 96
#
map rule bmr_name
rule-prefix 2001:db8:1::1 prefix-length 48 ipv4-prefix 1.1.1.0 prefix-length 24 ea-length 16 psid-offset 4
#
map-t instance 1 id 1
dmr-prefix dmr_name
map-rule bmr_name
#
ipv6 prefix pre1 delegation
map rule bmr_name
ipv6 pool pool1 bas delegation
prefix pre1
option-s46 dmr-prefix dmr_name
#
aaa
domain map-t
authentication-scheme default0
accounting-scheme default0
ipv6-pool pool1
#
dhcpv6 duid 0001000125a7625df063f9761497
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8
undo negotiation auto
undo shutdown
ipv6 enable
ipv6 address auto link-local
bas
access-type layer2-subscriber default-domain authentication map-t
authentication-method-ipv6 bind
#