Basic NAT64 Concepts
Basic NAT64 Elements
IPv6 prefix
IPv6 service data packets arriving at a NAT64 device carry IPv6 addresses, regardless of whether the packets are destined for IPv4 or IPv6 networks. In this case, the NAT64 device identifies destinations based on IPv6 prefixes that have been defined for NAT64 processing.- If the IPv6 prefix carried in a packet is the same as that defined on the NAT64 device, the packet is destined for an IPv4 network. After the NAT64 device processes the packet, the packet is forwarded to the IPv4 network.
- If the IPv6 prefix carried in a packet differs from that defined on the NAT64 device, the packet is destined for an IPv6 network. This packet is forwarded to the IPv6 network without being processed by NAT64.
The NAT64 device advertises the route with the defined IPv6 prefix. IPv4 packets that IPv6 terminals send and are destined for IPv4 networks are directed to the NAT64 device over the advertised route.
NAT64 Translation Principles
NAT64 performs translation in either PAT or No-PAT mode:
- PAT: A NAT64 device translates multiple IPv6 addresses and port numbers to an IPv4 address and a port number, respectively. The PAT mode enables multiple-to-one address mappings. Address mappings are distinguished based on port numbers. This mode is commonly used in NAT64 translation.
- No-PAT mode: A NAT64 device translates IPv6 addresses to IPv4 addresses, without processing port numbers. The No-PAT mode enables one-to-one mappings.
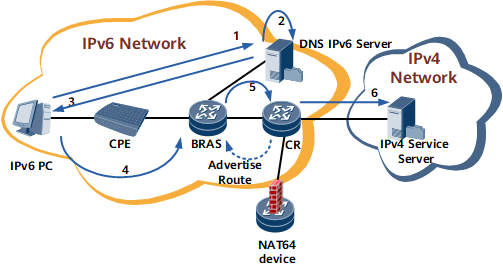
Figure 1 shows the NAT64 PAT networking.
- An IPv6-only PC sends an AAAA request to access a website at www.huawei.com to a DNS IPv6 server.
- The IPv6 network does not have the AAAA address of the website at www.huawei.com. The DNS IPv6 server resolves the A address of the URL and obtains 10.10.0.11.
- The DNS IPv6 server adds a specified IPv6 prefix of 64:FF9B before the IPv4 address carried in the A request to form an IPv6 address of 64:FF9B::0A0A:B as an AAAA resolution result. The server returns the IPv6 address to the PC.

The NAT64 device cannot be connected to a DNS64 server with a non-0 suffix. Relevant standards recommended the suffix of 0 for a DNS IPv6 server.
- The PC sends packets with source address 2001:DB8::1 and source port number 1500 to a destination with destination address 64:FF9B::0A0A:B and destination port number 80.
- Packets are forwarded to the NAT64 device.

The NAT64 device advertises a route destined for 64:FF9B/96 to direct traffic with the same destination to the NAT64 device.
- The NAT64 device removes the IPv6 prefix (64:FF9B) from the destination address of IPv6 packets and translates the source IP address and source port to 192.168.113.1 and 2000, respectively, in IPv4 packets and forwards them to the IPv4 network.
 When private network traffic is processed by NAT64 in the forward direction, the NAT64 device creates an entry in the NAT64 mapping table. The entry contains the following information:
When private network traffic is processed by NAT64 in the forward direction, the NAT64 device creates an entry in the NAT64 mapping table. The entry contains the following information:- Address mapping: A private IPv6 address of 2001:DB8::1 is mapped to a public IPv4 address of 192.168.113.1.
- Port mapping: A private port number of 1500 is mapped to a public port number of 2000.
If public network traffic is sent to the private network, traffic hits the entry and NAT64 reversely translates IPv4 information to IPv6 information. Obtained IPv6 packets are sent to the IPv6 network.