NAT64 ALG
The NAT64 application level gateway (ALG) provides transparent translation for some application layer protocols in NAT64.
Packets of some protocols such as ICMP and FTP carry IP addresses or port numbers in their payload. After NAT is performed, the IP address and port number in the TCP/UDP header are different from those in the payload, causing communication errors. For example, an FTP server using an internal IP address may be required to send its IP address to an external network host when communicating with the external network host. The internal IP address is encapsulated in the Data field of IP packets, which cannot be translated by NAT64. The external network host then uses the internal IP address carried in the IP packet payload and finds that the FTP server is unreachable.
A good way to solve the NAT64 issue for these special protocols is to use the Application Level Gateway (ALG) function. As a special conversion agent for application protocols, the NAT64 ALG interacts with the NAT device to establish states. It uses NAT state information to change the specific data in the Data field of IP packets and complete other necessary work, so that application protocols can run across internal and external networks.
For example, when an error occurs in packet A which is sent from a host on a private network to a public network, an ICMP unreachable packet is returned. The ICMP packet carries the header of the error packet A. Because the address is translated by a NAT64 device before packet A is sent, the source address is not the actual address of the host. If ICMP ALG is enabled, the ALG interacts with the NAT64 device before the ICMP packet is forwarded. The ALG translates the address in the Data field of packet A to the actual address of the host and completes other necessary work, so the NAT64 device can send the ICMP packet to the host.
NAT64 supports ALG for ICMP, FTP, HTTP, and UDP-based DNS.
NAT64 ALG for ICMP
NAT64 ALG translates the IP/ICMP packet header, and IP address and port number in the ICMP payload.
NAT64 ALG for FTP
- The FTP server is deployed on the IPv4 network. IPv6 users send EPRT requests to access the FTP server. The NAT64 device needs to convert EPRT requests into PORT requests and translates IPv6 addresses into the IPv4 addresses. The NAT64 device delivers the Servermap table to the forwarding plane so that data traffic on the IPv4 network can be transmitted.
- The FTP server is deployed on the IPv4 network. IPv6 users send EPSV requests to access the FTP server. The NAT64 device needs to convert EPSV requests into PASV requests and translates IPv4 addresses of EPSV responses into the IPv6 addresses.
NAT64 ALG for HTTP
- 301 Moved Permanently: indicates that requested resources are permanently available in the redirect-to URL. The new URL is carried in the Location header.
- 302 Found: indicates that requested resources are temporarily available in the redirect-to URL. The redirect-to URL may change sometimes. The new URL is carried in the Location header.
The response contains the Location header field. The Location header field is used to complete the request or identify a new resource so that receivers can redirect to the URL specified by the Location header field but not the requested URL. If the URL in the Location header field contains the IPv4 address, the NAT64 device needs to convert IPv4 addresses into IPv6 addresses.
NAT64 ALG for DNS
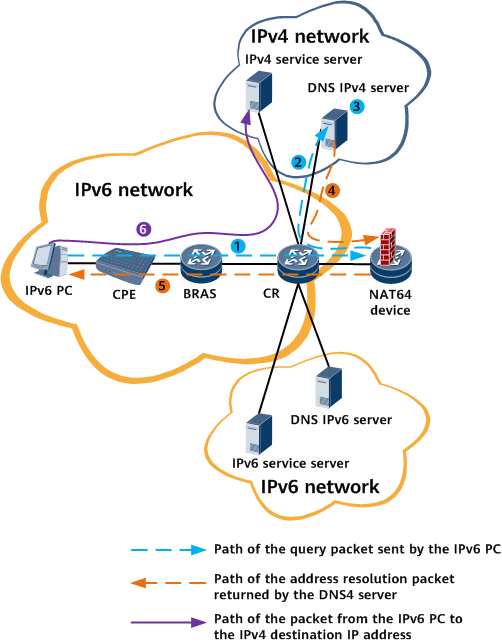
If a network has only the DNS4 server deployed, NAT64 ALG is required to obtain IPv4 addresses. Figure 1 shows the networking and data traffic paths.
- An IPv6 terminal sends DNS AAAA query request record packet to the IPv4 network.
- After the query request reaches the DNS ALG of the NAT64 device, the DNS ALG converts AAAA record into A record and sends it to the DNS4 server on the IPv4 network.
- The DNS4 server on the IPv4 network completes domain name resolution and returns a resolution result. In this case, the DNS4 server obtains the IPv4 address mapping the domain name.
- When the resolution result reaches the DNS ALG of the NAT64 device, the DNS ALG converts A record response into AAAA record response, converts the IPv4 address into the IPv6 address, and saves the mapping locally. The obtained IPv4 address is mapped to the IPv6 address by the DNS ALG.
- After receiving the IPv6 destination address resolution result from the NAT64 device, the IPv6 terminal can access the IPv4 destination address.