NAT64 Deployment
NAT64 applies to the latter phase of IPv6 transition in which IPv6 is the mainstream application. New users connected to an IPv6 network can access the remaining IPv4 services across the IPv6 network.
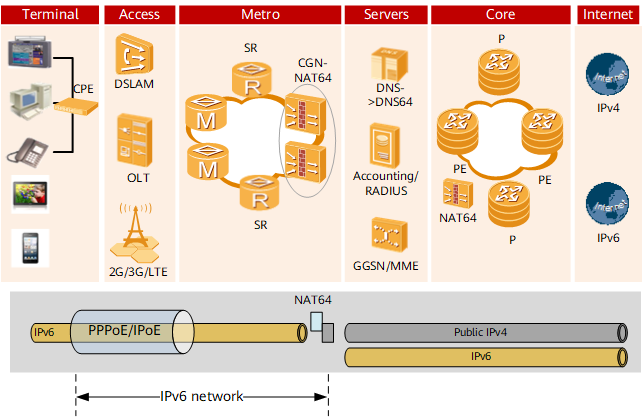
On the network shown in Figure 1, the CGN device is deployed on the SR/CR side, and the CPE, CR, and CGN device communicate with each other over an IPv6 network. The terminal users of the IPv6 access translate IPv6 addresses into public IPv4 addresses to access the IPv4 service.
A CGN device can be deployed to the SR or CR.
The IPv6 terminal sends an AAAA request to a website URL to the DNS64 server over the IPv6 network. As the IPv6 network does not have the AAAA address of the website URL, the DNS64 server obtains the parsing result of address A of the URL address. The DNS64 server adds an IPv6 prefix (such as 64:FF9B::/96) to the IPv4 address returned in the A request and adds the IPv6 AAAA parsing result to the IPv6 prefix to the terminal.
After obtaining the DNS response, the terminal accesses the IPv6 address of the Ipv6 prefix.
Based on the IPv6 prefix route, the NAT64 CGN device removes the IPv6 prefix of the IPv6 packet destination address and performs NAT64 on the source IP address and port number and translate to Ipv4 addresses before forwarding them to the IPv4 network.
IPv4 packets are forwarded to the NAT64 device and then to the terminal user after the IPv4-IPv6 stateful translation.
If the DNS64 server is unavailable, DNS ALG needs to be enabled for the NAT64 instance.