Basic NAT Processes
Basic Concepts
Before the basic NAT process is introduced, familiarize yourself with the following concepts:
NAT service board: is a physical board that has the NAT capability.
NAT address pool: is an address pool used to manage NAT address resources.
NAT traffic diversion: uses diversion rules to identify user packets that need to be translated using NAT and direct the packets to a NAT service board for NAT translation.
NAT instance: is a service configuration unit that is bound to NAT service boards, address pools, and other NAT attributes.
Basic Process
The following figure shows the forward and reverse NAT implementation processes. The implementation varies according to deployment modes, address pool types, and traffic diversion modes. The following sections describe NAT classification, NAT address pool and its conversion basis, and NAT port allocation.
NAT Conversion
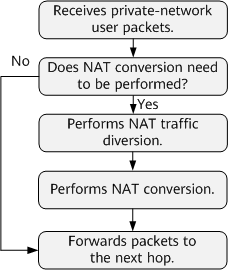
After receiving packets, the device checks whether NAT is required.
The NetEngine 8000 F filters the user packets that need to be processed by NAT based on an ACL bound to the traffic diversion policy.- If user packets match the ACL, NAT traffic diversion is performed.
- If the user packets do not match the ACL, the device forwards the packet based on the common packet forwarding process.
- The NetEngine 8000 F diverts the user packets to the NAT service board bound to the NAT instance for translation.
- The NetEngine 8000 F selects the IP address and port number from the address pool and port range bound to the NAT instance to replace the existing source IP address and port number in the user packet to implement NAT.
- After the translation, the user packets are forwarded to the next hop based on the regular forwarding process.
Reverse NAT Conversion
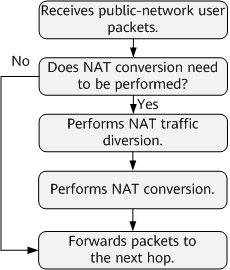
After receiving a packet, the NetEngine 8000 F determines whether to perform reverse NAT translation.
The NetEngine 8000 F filters the user packets in FIB traffic diversion mode and diverts user packets that need to be translated to a NAT service board for translation.- If the destination address in the user packet matches a NAT address pool route in the FIB table, the NetEngine 8000 F performs reverse NAT.
- If the destination address of a user packet matches a route of another type, the NetEngine 8000 F forwards the packet based on the regular packet forwarding process.
- The NetEngine 8000 F diverts the packets that require NAT reverse translation to the NAT service board.
- The NAT service board performs reverse translation on user packets based on NAT mapping entries. The destination IP address and port number in each user packet are replaced with a private IP address and a port number.
- After reverse NAT is performed, user packets are forwarded to the next hop based on the regular forwarding process.