BA and PHB
BA and PHB Actions
- The service-class and color of a packet is initialized to <BE, Green>.
- If the trust upstream command is configured on the inbound interface, when received a packet, the upstream (inbound) board of the device resets the service-class and color of the packet based on the priority field(s) (such as DSCP, 802.1p, EXP, and so on) of the packet. This procedure is called BA action.
- If remark, or remark within CAR, is configured for the packet, the inbound board resets the service-class and color of the packet.
- Then, the device takes other QoS actions based on the service-class and color of the packet.
- After the above actions are taken, the downstream (outbound) board should decide whether to modify the priority field(s) (such as DSCP, 802.1p, EXP, and so on) of the packet or not. In some scenarios, the priority field of the packet is not expected to be changed. The procedure that the outbound board modifies the priority field(s) of the packet based on the service-class and color of the packet is called PHB action.Figure 1 BA and PHB actions
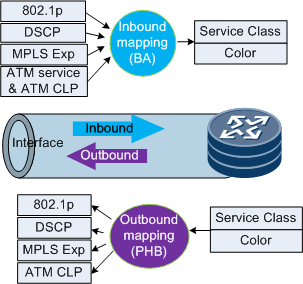
BA and PHB Symbols
A device sets two markers on each interface to determine whether to implement reverse mapping for outgoing packets.
- Marker 1: BA. BA is enabled on the inbound interface and is carried in internally added packet headers and transmitted to the outbound interface through the switching module.
- Marker 2: PHB. PHB is enabled on the outbound interface.
The device takes PHB action only when both the two symbols are set as "Y".
By default, the "BA-symbol" is set as "N", and the "PHB-symbol" is set as "N".
Both the "BA-symbol" and "PHB-symbol" can be changed by commands (Table 1).
Command |
QoS Action |
Values of the "BA-symbol" and "PHB-symbol" |
|---|---|---|
trust upstream |
The board takes BA action for inbound packets and takes PHB action for outbound packets. |
Both the "BA-symbol" and "PHB-symbol" are set as "Y". |
diffserv-mode { pipe | short-pipe } |
The board takes BA action for inbound packets. |
|
diffserv-mode uniform |
This command is default configuration and does not affect the actions of the inbound and outbound boards. |
Both the "BA-symbol" and "PHB-symbol" keep unchanged. |
service-class |
|
|
remark (inbound) |
The "BA-symbol" is set as "Y" and the "PHB-symbol" is not affected. The inbound board takes BA action and remarks the inbound packets, regardless of the "BA-symbol" and "PHB-symbol". |
|
remark (outbound) |
The outbound board remarks the outbound packets, regardless of the "BA-symbol" and "PHB-symbol". For example, assume that the remark dscp 11 command is configured for outbound interface and the service-class and color of the packet are <ef, green>. The DSCP of the packet is set as 11 directly, rather than the value mapped from <ef, green> based on the downstream PHB mapping table. If the outbound packet has vlan tag, the 802.1p of the vlan tag is set based on <ef, green> and the downstream PHB mapping table. If both the remark dscp 11 command and the remark 8021p command are configured for the outbound interface, then both the DSCP and the 802.1p of the packet are modified directly according to the remark commands. |
|
qos phb enable |
- |
The "PHB-symbol" is set as "Y". |
qos phb disable |
- |
The "PHB-symbol" is set as "N". |
qos car { green | yellow | red } pass service-class color |
The service-class and color of the packet are reset. |
Both the "BA-symbol" and "PHB-symbol" keep unchanged. |
Rules for PHB Action
To set BA-symbol as "Y", configure the "trust upstream", "remark", "service-class" command on inbound interface.
To set BA-symbol as "N", configure the "service-class class-value color color-value no-remark" command, or do not configure the four commands stated above on the inbound interface.
To set PHB-symbol as "Y", configure the "trust upstream" or "qos phb enable" command on outbound interface.
To set PHB-symbol as "N", configure the "qos phb disable" command or do not configure the "trust upstream" command on outbound interface.
BA-symbol |
PHB-symbol |
PHB Action |
|---|---|---|
N |
N |
No |
Y |
N |
No |
Y |
Y |
Yes |
Which QoS Priority Field is Trusted If a Packet Carries the DSCP, 802.1p, and MPLS EXP Fields
The trusted QoS priority fields depend on the configuration on the inbound interface. For details, see Table 3.
Inbound Interface Configuration |
Packet Type |
Which Field Is Trusted |
|
|---|---|---|---|
trust upstream |
trust 8021p |
||
× |
× |
Any types |
No field is trusted and the packet is mapped to <BE, Green>. |
× |
√ |
||
√ |
× |
IPoE, IPoVLAN, IPoQinQ |
DSCP |
IPoPPP, IPoHDLC, IPoFR |
DSCP |
||
MPLS |
Outer EXP (if EXP, 802.1p, and DSCP are all available, EXP is also selected) |
||
Other types |
No field is trusted.
|
||
√ |
√ |
VLAN |
802.1p |
QinQ |
802.1p in outer VLAN |
||
MPLS |
If EXP, 802.1p, and DSCP are all available, select 802.1p. |
||
Others |
No field is trusted and the packet is mapped to <BE, Green>. |
||
NOTE:
"Other types" here indicates neither IP nor MPLS packets when the outer L2 header is removed. |
|||
Which Priority Field of the Inbound Packet Is Reset in PHB Action
Outbound Interface Configuration |
Priority Field Re-marked in PHB Action |
|
|---|---|---|
trust upstream |
trust 8021p |
|
Not configured |
Not configured |
No field is re-marked. |
Not configured |
Configured |
No field is re-marked. |
Configured |
Not configured |
|
Configured |
Configured |
|
Rules for Marking the 802.1p Field of New-added VLAN Tag
When a VLAN header is added to a packet after the packet passes through a device, the setting of the 802.1p value depends on the PHB-symbol status.
PHB-symbol |
Rules for marking the 802.1p field of the new-added VLAN tag |
|---|---|
Y |
According to the <service-class, color> of the packet and the downstream priority mapping table. |
N |
Marked as 0. |
Rules for Marking the EXP Field of the New-added MPLS Header
When an MPLS header is added to a packet after the packet passes through a device, the setting of the EXP value depends on the PHB-symbol status.
PHB-symbol |
Rules for Marking the EXP Field of the New-added MPLS Header |
|---|---|
Y |
Both inner and outer EXP: according to the <service-class, color> of the packet and the downstream priority mapping table. |
N |
|