Example for Configuring SZTP
Networking Requirements
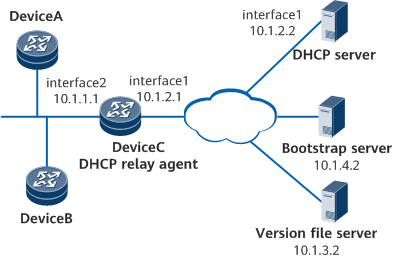
On the network shown in Figure 1, DeviceA and DeviceB are two new unconfigured devices connected to DeviceC, which functions as the egress gateway of DeviceA and DeviceB. There are reachable routes between DeviceC and the DHCP server, bootstrap server, and version file server.
Configuration Roadmap
Configure a DHCP server.
- Configure a DHCP relay agent.
- Configure a bootstrap server.
- Configure a version file server.
Power on DeviceA and DeviceB to start the SZTP process.
Procedure
- Configure a DHCP server. Specifically, configure an IP address pool for the DHCP server to allocate IP addresses to clients, and configure DHCP server options by referring to Table 1. For configuration details, see the DHCP server configuration in the corresponding product documentation. The HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F Series is used as an example.
Table 1 Values of DHCP server options Option ID
Description
Value
1
Subnet mask of an IP address
255.255.225.0
3
Egress gateway of a DHCP client
10.1.1.1
143
Bootstrap server address
10.1.4.2
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DHCP_Server [*HUAWEI] commit [~DHCP_Server] dhcp enable [*DHCP_Server] ip pool pool1 [*DHCP_Server-ip-pool-pool1] gateway 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [*DHCP_Server-ip-pool-pool1] section 1 10.1.1.1 10.1.1.255 [*DHCP_Server-ip-pool-pool1] option 143 hex 001268747470733a2f2f31302e312e342e323a31 [*DHCP_Server-ip-pool-pool1] quit [*DHCP_Server] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*DHCP_Server-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 [*DHCP_Server-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*DHCP_Server] commit
- Configure a DHCP relay agent.
# Configure the DHCP relay function on DeviceC. Set the IP address of the interface connecting DeviceC to DeviceA and that of the interface connecting DeviceC to DeviceB to 10.1.1.1 so that DeviceC functions as the default gateway of DeviceA and DeviceB.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DeviceC [*HUAWEI] commit [~DeviceC] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [~DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [~DeviceC] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/2 [~DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] dhcp select relay [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] ip relay address 10.1.2.2 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] commit [~DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit
- Configure a bootstrap server.
# Huawei devices cannot function as a bootstrap server. In SZTP networking, a third-party server needs to be deployed. For configuration details, see the documentation of the third-party server.
# The bootstrap server must be embedded with the Huawei level-2 CA certificate, ownership voucher, and owner certificate.
# On the bootstrap server, set the IP address of the version file server to 10.1.3.2, and set the version files, configuration files, and their paths for DeviceA and DeviceB.
- Configure a version file server.
# Huawei devices cannot function as a version file server. In SZTP networking, a third-party server needs to be deployed. For configuration details, see the documentation of the third-party server.
# After configuring the version file server, save the version files and configuration files to be loaded to the device to the specified path on the bootstrap server.
- Power on DeviceA and DeviceB to start the SZTP process.
- Verify the configuration.# After the device is started, log in to it and run the display startup command to check whether the system software and configuration file are as expected. The following shows the command output of DeviceA.
<DeviceA> display startup MainBoard: Configured startup system software: cfcard:/V800R021C00SPC100B140_0424_new.cc Startup system software: cfcard:/V800R021C00SPC100B140_0424_new.cc Next startup system software: cfcard:/V800R021C00SPC100B140_0424_new.cc Startup saved-configuration file: cfcard:/vrpcfg.cfg Next startup saved-configuration file: cfcard:/vrpcfg.cfg Startup paf file: default Next startup paf file: default Startup patch package: cfcard:/NetEngine 8000 FV800R021C00SPC100.PAT Next startup patch package: cfcard:/NetEngine 8000 FV800R021C00SPC100.PAT
Configuration Files
- DeviceC configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 dhcp select relay ip relay address 10.1.2.2 # return
- DHCP server configuration file
# sysname DHCP_Server # dhcp enable # ip pool pool1 gateway 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 section 1 10.1.1.1 10.1.1.255 option 143 hex 001268747470733a2f2f31302e312e342e323a31 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 # return