URPF Overview
URPF prevents network attacks based on source address spoofing and can be performed in strict or loose mode.
Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (URPF) is a technology used to defend against network attacks based on source address spoofing.
Generally, upon receiving a packet, a router first obtains the destination IP address of the packet and then searches the forwarding table for a route to the destination address. If the router finds such a route, it forwards the packet; otherwise, it discards the packet. A URPF-enabled router, however, obtains the source IP address of a received packet and searches for a route to the source address. If the router fails to find the route, it considers that the source address is a forged one and discards the packet. In this manner, URPF can effectively protect against malicious attacks that are launched by changing the source addresses of packets.
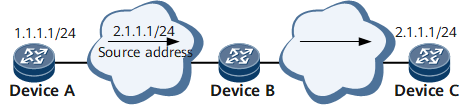
DeviceA generates a packet with a pseudo source IP address 2.1.1.1 and sends the packet to DeviceB. DeviceB sends a response packet to DeviceC whose IP address actually is 2.1.1.1. In this manner, DeviceA attacks both DeviceB and DeviceC by sending illegal packets.
URPF can be applied on the upstream inbound interfaces of the router, including two application environments: single-homed client and multi-homed client.
Single-homed client
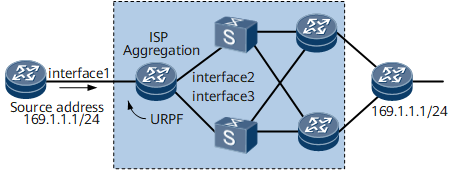
Figure 2 shows the connection between the client and the aggregation router of the ISP. Enable URPF on interface1 of the ISP router to protect the router and Internet from source address spoofing attacks from the client network.
Multi-homed client
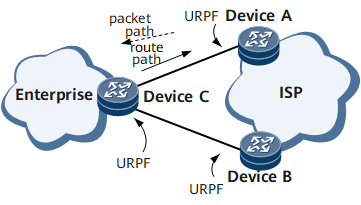
URPF can be applied in the case that multiple connections are set up between the client and the ISP, as shown in Figure 3. For URPF, ensure that the links between the client router and the ISP router that the packets from the client to a host on the Internet and the packets from the host to the client traverse are identical. That is, you need to ensure the route symmetry. Otherwise, URPF discards certain normal packets because of interface unmatching.
Multi-homed client and multi-ISP
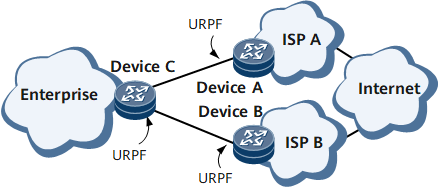
URPF can be applied in the case that a client is connected to multiple ISPs, as shown in Figure 4. In this case, route symmetry has to be ensured.
URPF applied in the scenario where a client is connected to multiple ISPs has the following features:
If route symmetry cannot be ensured, you can use the loose check. That is, URPF does not check the consistency of the interfaces and as along as a route contains the source address of the packet, the packet can pass.
The routers of multiple users may have only one default route to the router of the ISP. Therefore, matching the default route entry needs to be supported.
As the security system on the ingress, URPF is better than the conventional firewall in performance.