Fundamentals of Mirroring
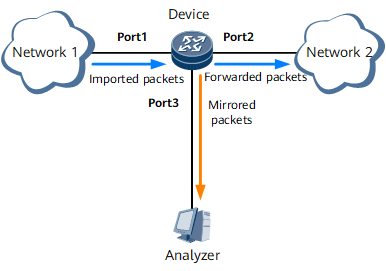
Local mirroring allows a device to copy traffic on an interface and export the traffic through another interface. As shown in Figure 1, port 1 is a local mirrored port and port 3 is a local observing port.
- Port mirroring: All traffic sent and received by a port is mirrored.
- Flow mirroring: Traffic is mirrored only when it matches a configured filter rule.
Supported Local Mirroring Features
Mirrors data that is sent or received by a physical port.
Mirrors packets received by a mirrored port and sends the packets through a specified observing port.
Mirrors packets sent by a mirrored port and sends the packets through a specified observing port.
- Packets received or sent by a mirrored port can be mirrored to either the same observing port or different observing ports.
Mirrors data that is sent or received by a VLAN sub-interface.
Mirrors Ethernet packets only containing an outer tag equal to a specified VLAN ID and sends these packets through a specified observing port to filter packets based on their VLAN IDs.
Mirrors data based on traffic classification.
Mirrors packets that match multi-field (MF) classification rules, such as rules with specified source IP addresses and destination IP addresses, and then sends them through a specified observing port.
Performs the CAR function for mirrored traffic.
Sets the committed information rate (CIR) to minimize the impact of mirrored packets on regular forwarding.
Mirrors packets to be sent to the CPU.
Mirrors only the packets that are sent to the CPU and sends the packets through a specified observing port.
Removes labels from packets on an observing port.
Allows an observing port to remove a maximum of two labels from mirrored packets. This function is supported only by main ports that function as observing ports.
Configures whether a mirrored packet carries a Layer 2 header in local mirroring.
Allows a sub-interface functioning as an observing port to remove the Layer 2 header from an original packet. Then the observing port sends packets merely carrying Layer 1 and Layer 2 headers.
Supports packet mirroring filter rules.
Supports filter rule configurations and filters packets based on filter rules.
- Mirrors packet content based on a specified length.
- Sets a length for packet content to be mirrored.