Application Scenarios for 1588v2 , SMPTE-2059-2 and G.8275.1
Currently, 1588v2 is applicable to a link where all devices are 1588v2-capable, and a maximum of 30 hops are supported.
Because a master clock has multiple slave clocks, it is recommended that you use the BITS or IP clock server as the master clock. It is not recommended to use any device as the master clock because the CPU of the device may be overloaded.
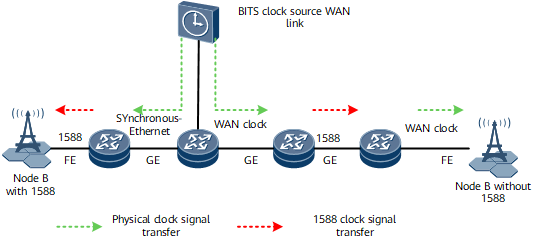
1588v2 Clock Synchronization in Hop-by-Hop Mode
As shown in Figure 1, the clock source can send clock signals to NodeBs through the 1588v2 clock, WAN clock, synchronous Ethernet clock, or any combination of clocks.
Scenario description:
NodeBs only need frequency synchronization.
GE links on the bearer network support the 1588v2 clock rather than the synchronous Ethernet clock.
Solution description:
The Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) or synchronous Ethernet clock sends stratum 3 clock signals through physical links. On the GE links that do not support the synchronous Ethernet clock, stratum 3 clock signals are transmitted through 1588v2.
Advantage of the solution: The solution is simple and flexible.
Disadvantage of the solution: Only frequency synchronization rather than time synchronization is performed.
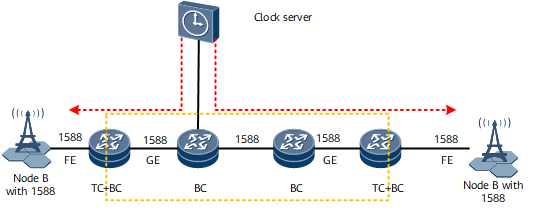
1588v2 Clock Synchronization in Bearer and Wireless Networks in the Same Clock Domain
Scenario description:
NodeBs need to synchronize time with each other.
The bearer and wireless networks are in the same clock domain.
Solution description:
The core node supports GPS or BITS clock interfaces.
All nodes on the bearer network function as BC nodes, which support the link delay measurement mechanism to handle fast link switching.
Links or devices that do not support 1588v2 can be connected to devices with GPS or BITS clock interfaces to perform time synchronization.
Advantage of the solution: The time of all nodes is synchronous on the entire network.
Disadvantage of the solution: All nodes on the entire network must support 1588v2.
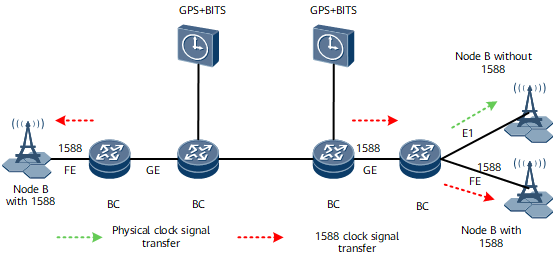
1588v2 Clock Synchronization in Bearer and Wireless Networks in Different Clock Domains
Scenario description:
NodeBs need to synchronize time with one another.
The bearer and wireless networks are in different time domains.
Solution description:
The GPS is used as a time source and is connected to the wireless IP clock server.
BCs are deployed in the middle of the bearer network to synchronize the time of the intermediate network.
TCs are deployed on both ends of the bearer network. TCs only correct the message transmission delay and send the time to NodeBs, but do not synchronize the time with the clock server.
Advantage of the solution: The implementation is simple because the bearer network does not need to synchronize with the clock server.
Disadvantage of the solution: Devices on both ends of the bearer network need to support 1588v2 in TCandBC mode.
G.8275.1 Per-Hop Clock Synchronization
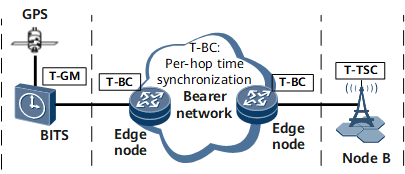
Scenario description:
NodeBs need to synchronize time with one another.
The bearer and wireless networks are in the same clock domain.
Solution description:
Core nodes support GPS/BITS interfaces.
Network-wide time synchronization is achieved from the core node in T-BC mode. All T-BC nodes support path delay measurement to adapt to fast link switching.
Network-wide synchronization can be traced to two grand masters.
The advantage of the solution is that the network-wide time is synchronized to ensure the optimal tracing path.
The disadvantage of the solution is that all nodes on the network need to support 1588v2 and G.8275.1.
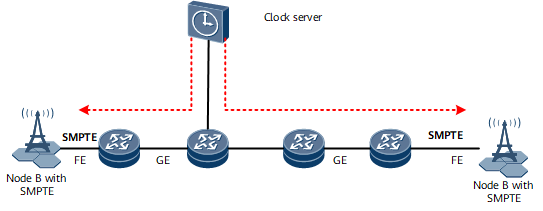
SMPTE-2059-2 E2E Clock Synchronization
As shown in Figure 5, the clock server and the base station transmit TOP-encapsulated SMPTE-2059-2 packets over a bearer network enabled with QoS assurance (jitter < 20 ms).
Scenario Description
NodeBs require only frequency synchronization.
The bearer network does not support SMPTE-2059-2 or the use of SyncE to restore frequency.
Solution Description
Bearer network devices are connected to the wireless IP clock server, and SMPTE-2059-2 is used to transmit and restore clock in E2E mode.
The clock server sends timing messages in the SMPTE-2059-2 format. The bearer network transparently transmits the timing messages. Upon receipt of the timing messages, NodeBs restore clock information.
SMPTE-2059-2 packets are transparently transmitted over the bearer network by priority to ensure an E2E jitter of less than 20 ms.
Solution advantage: This solution is simply, with no need for bearer network devices to support SMPTE-2059-2.
Solution disadvantages: Only frequency synchronization rather than time synchronization is supported. An E2E jitter of 20 ms is hard to guarantee.