Overview of URPF
Definition
Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (URPF) is a technology used to defend a network against attacks that are based on source address spoofing.
Generally, when receiving a packet, a router first obtains the destination IP address of the packet and then searches the forwarding table for a route leading to the destination address. If the router finds such a route, it forwards the packet; otherwise, it discards the packet. A URPF-enabled router, however, obtains the source IP address of a received packet and searches for a route leading to the source address. If the router fails to find the route, it considers the source address to be forged and discards the packet. In this manner, URPF can effectively protect the system against malicious attacks that are launched by changing the source addresses of packets.
To ensure that URPF runs normally, symmetric routing is required. That is, packets from a user to a host on the Internet and packets from the host on the Internet to the user must be transmitted along the same path between the user's router and Internet Service Provider (ISP) router. Otherwise, URPF incorrectly discards some normal packets because of mismatched interfaces.
Purpose
Source address spoofing has become a common type of attack on the Internet. URPF was developed to solve network security problems caused by source address spoofing.
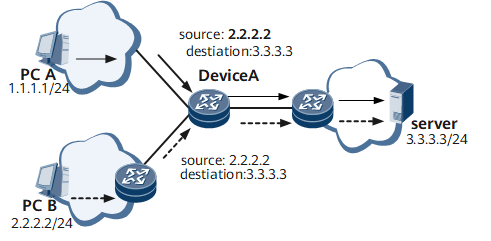
In the example shown in Figure 1, PC A forges a request packet with the bogus source address 2.2.2.2 and sends it to the server. After receiving the request packet, the server sends a response packet to PC B at 2.2.2.2. Then the forged packet sent by PC A attacks the server and PC B.
A large number of such forged packets form a Denial of Service (DoS) attack, which has a substantial impact on networks.
Therefore, source address spoofing needs to be addressed on the ingress of a network. URPF can be used to prevent network security problems caused by source address spoofing.

URPF can defend the system against DOS attacks of both IPv4 and IPv6 packets.
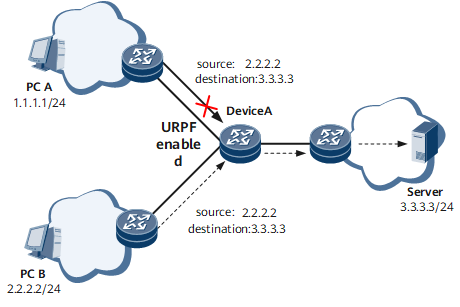
In the example shown in Figure 2, after URPF is enabled on Device A, forged packets sent by PC A are directly discarded by Device A, and packets sent by PC B are normally forwarded by Device A.
As a security mechanism applied on the ingress of a network, URPF is better than traditional firewalls in terms of performance.
Benefits
URPF offers the following benefits:
Effectively solves the problem of source address spoofing on the ingress of a network. After the network ingress enabled with URPF filters out the packets with forged source addresses, the source IP addresses of the remaining attack packets are valid ones. Therefore, it is easy to find out the attack sources.