AAA
Basic Structure
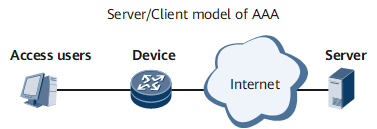
Using the client/server model, AAA has good extensibility and facilitates centralized management over user information. Figure 1 shows the basic AAA structure.
Authentication
AAA supports the following authentication modes:
- Non-authentication: Users are completely trusted, and validity check is not performed. This mode is rarely used.
- Local authentication: In this mode, user information, including the user name, password, and attributes, is configured on a Network Access Server (NAS). Local authentication features fast processing speeds at low operation cost. However, the information storage capacity is limited to the capacity of device hardware.
- Remote authentication: In this mode, user information, including user name, password, and attributes, is configured on an authentication server. AAA can remotely authenticate users through the Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) protocol. As the client, the NAS communicates with the RADIUS server.
In addition, the three authentication modes can be combined.
- Remote authentication when local authentication fails: In this mode, local authentication takes precedence. Remote authentication is performed only after local authentication fails.
- Local authentication when there is no response to remote authentication: In this mode, remote authentication takes precedence. If the AAA server does not respond, local authentication is performed.
- Non-authentication when there is no response to remote authentication: In this mode, remote authentication takes precedence. If the AAA server does not respond, non-authentication is performed.
Authorization
AAA supports the following authorization modes:
- Non-authorization: No authorization is performed.
- Local authorization: Users are authorized based on the attributes of local user accounts configured on the NAS.
- If-authenticated authorization: Users pass authorization after passing authentication (local or remote authentication).
- RADIUS authorization: Users pass RADIUS authorization after passing RADIUS authentication. In other words, RADIUS integrates authentication and authorization. Therefore, RADIUS authorization cannot be performed separately.
Authorization for online users
The BRAS supports dynamic authorization for online users.
In dynamic authorization, attributes such as the user group, committed access rate (CAR), and policy name, are re-configured on the AAA server. The AAA server then delivers the attributes to the AAA module through Change of Authorization (CoA) packets and the AAA module dynamically updates the users' authorization information.
Accounting
AAA supports the following accounting modes:
- Non-accounting: Users are not charged.
- Remote accounting: Remote accounting is performed through the RADIUS server.