Overview of AAA and User Management
Definition
- Authentication: checks whether a user has the rights to access the network.
- Authorization: authorizes a user so that the user can use a specified service.
- Accounting: records the usage of network resources for charging purposes.
Purpose
AAA provides authentication, authorization, and accounting for users.
Benefits
AAA offers the following benefits:
AAA enhances system security by preventing invalid login.
RADIUS
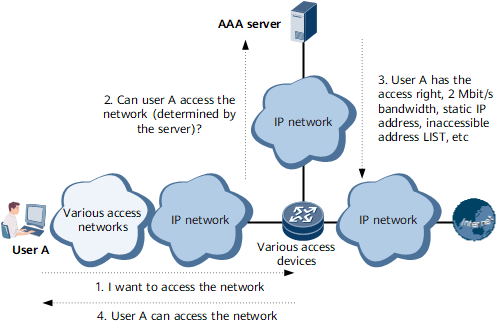
As one of the commonly-used protocols that implement AAA, Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) was initially used to manage a large number of geographically-dispersed users that use serial ports and modems. Now it is widely used in the Network Access Server (NAS) system.
In a NAS system, a user must set up a connection with the NAS through a network, such as a telephony network, to obtain the rights to access certain networks or to use certain network resources. In this case, the NAS is in charge of authenticating the user or the connection.
Specifically, the NAS sends the user information to the RADIUS server. RADIUS prescribes how to transmit the user information and accounting information between the NAS and RADIUS servers. Upon receiving requests from users, the RADIUS server authenticates the users and then sends the required configuration information back to the NAS.
The authentication information is transmitted with key encryption between the NAS and RADIUS server to protect the user passwords on less secure networks.
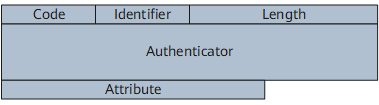
Figure 2 shows the format of a RADIUS packet.
A RADIUS packet has the following fields:
Code: indicates the message type, such as access request, access permit, or accounting request.
Identifier: contains numbers in ascending order. It is used to match the request packets and response packets.
Length: indicates the total length of all fields.
Authenticator: authenticates the reply from the RADIUS server.
Attribute: contains user-specific attributes.