EDSG Service Policy Obtainment
A service policy delivered by a server carries only the service policy name, and parameters must be obtained from a service policy. An EDSG service policy can be obtained in any of the following modes:
- Local: A service name is used as an index to obtain an EDSG service policy from the local configurations.
- RADIUS: A service name is used as a user name and authentication packets are used to obtain an EDSG service policy from a RADIUS server. The obtained EDSG service policy is cached to the local device and will not be deleted if it is referenced by any service instance. The EDSG service policy does not need to be repeatedly obtained.
- Local and then RADIUS: An EDSG service policy is first obtained from the local configurations. If no EDSG service policy is configured on the local device, an EDSG service policy is obtained from the RADIUS server.
- RADIUS and then local: An EDSG service policy is first obtained from the RADIUS server. If the RADIUS server has no response, a locally configured EDSG service policy is used.
Figure 1 EDSG service policy obtainment
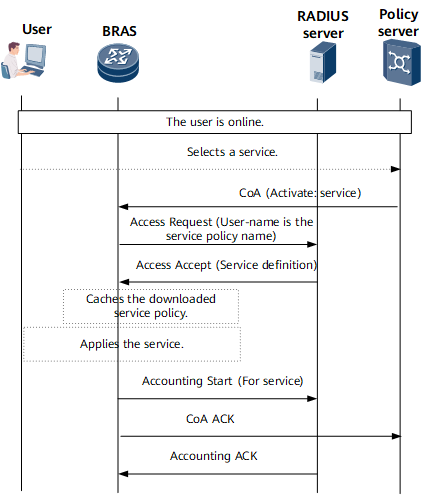

Periodic Update of a Cached EDSG Service Policy
You can configure an interval at which a cached EDSG service policy is updated. After the cached EDSG service policy reaches the configured interval, the BRAS re-obtains an EDSG service policy from the RADIUS server to update the cached EDSG service policy when a service is added.
Online Update of Service Policy Parameters
By default, service policy parameter updates do not affect generated service instances and apply only to service instances that are activated after an update.
You can manually specify a service policy name to forcibly update all service instance parameters to the latest service policy parameters.