BOD Overview
BOD is one of the value-added services. Therefore, this section introduces BOD by describing the value-added service process.
Composition of a value-added service system
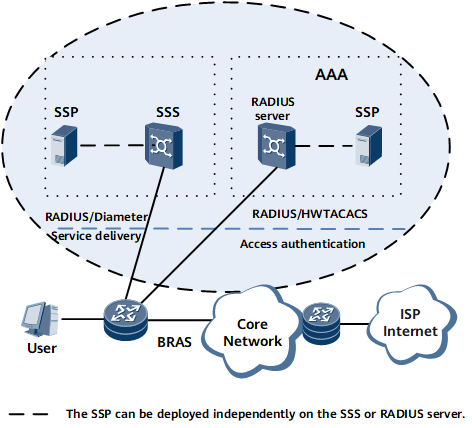
To implement value-added services, the following systems or devices are required:
Service Selection Server (SSS): As a Policy Decision Point (PDP), it is responsible for the configuration, management, policy decision, and accounting of value-added services.
AAA server: It is used for authentication, authorization, and accounting of access services
BRAS: As a Policy Enforcement Point (PEP), it is responsible for enforcing service policies, forwarding service flows, and providing original accounting information of each type of service for service-based accounting.
Service select portal (SSP): It is a Web-based self-help service portal, through which an operator demonstrates services and introduces services to users. The SSP can be a portal server, through which users can browse, subscribe to, and search for services.

The interfaces connecting the BRAS and an AAA server use RADIUS or HWTACACS; the interfaces connecting the BRAS and an SSS use RADIUS or DIAMETER.
Processing of Value-added Services
Value-added services are based on access services. When a user accesses a device, the policy server delivers the access service policy for the user. When using value-added services, the user needs to dynamically change the service policy.
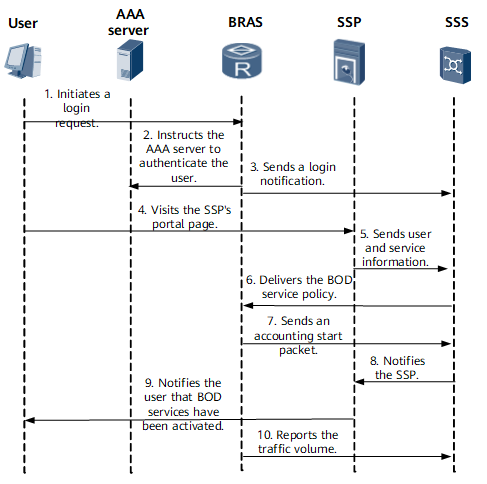
A user sends a login request.
The user is authenticated by the AAA server and successfully logs in.
The BRAS informs the SSS (Radius/Diameter) of the user information.
The user visits the Portal page and select the interested value-added services.
The SSP sends information about the user and the selected services to the SSS (Radius/Diameter).
The SSS customizes a service policy based on the selected services, and then sends the service policy to the BRAS by Radius or Diameter.
The BRAS implements the delivered service policy and instructs the SSS to start accounting.
After receiving the message of starting accounting, the SSS informs the SSP.
The SSP notifies the user through the Portal page that the selected services have been activated and can be used.
The user starts to use the value-added services. The BRAS accounts and controls the value-added services based on the service policy, and reports the traffic volume to the SSS.