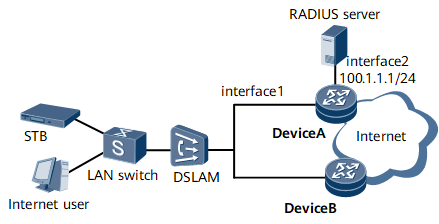
Typical Double-Edge Network with Multicast Virtual Scheduling
In a typical double-edge network that is configured with multicast virtual scheduling, the DeviceA needs only to implement virtual scheduling. Multicast data replication is implemented by the DeviceB.
The double-edge network shown in Figure 1 is similar to the single-edge network. DeviceA identifies all the service flows belonging to the same family according to the Option 82 information or outer VLAN information, and implements virtual scheduling of these services as a whole.
After detecting that the subscriber demands a multicast program and determining that virtual scheduling needs to be implemented, DeviceA adjusts the bandwidth for the subscriber's unicast traffic based on the bandwidth of the demanded multicast program and the total bandwidth of the subscriber. Then, DeviceB forwards the requested multicast traffic through the multicast VLAN, and the downstream device copies the multicast traffic to the subscriber.
In addition to forwarding multicast data to the subscriber, DeviceB also forwards the multicast data to DeviceA. DeviceA measures the received multicast data, and implements multicast virtual scheduling based on the measurement result.