Applications of 1588 ATR
1588 ATR establishes a clock link between a client and a server by exchanging Layer 3 unicast packets, and obtains the offset between the client and server clocks by exchanging PTP packets. In this way, the client clock can be synchronized with the server clock.
1588 ATR Time Synchronization Through Transparent Transmission
Figure 1 1588 ATR time synchronization through transparent transmission
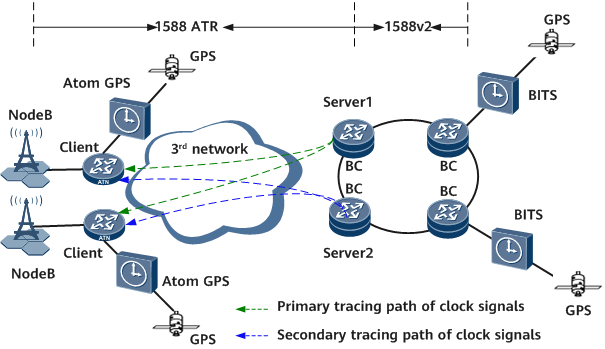

Scenario Description
- On an IP RAN, time synchronization is required between NodeBs.
- Third-party networks (such as microwave and switch networks) do not support 1588v2 time synchronization.
Solution Description
- You can configure 1588 ATR or an external Atom GPS timing module on the client to implement time synchronization across a third-party network. BCs support the 1588 ATR server function. After synchronizing the time with an upstream device, a BC can function as an ATR server to provide the time synchronization service for downstream NodeBs. A client can receive time synchronization information through the ATOM GPS time serving module or implement time synchronization through 1588 ATR transparent transmission.
Hop-by-Hop 1588 ATR Time Synchronization
Figure 2 Hop-by-hop 1588 ATR time synchronization
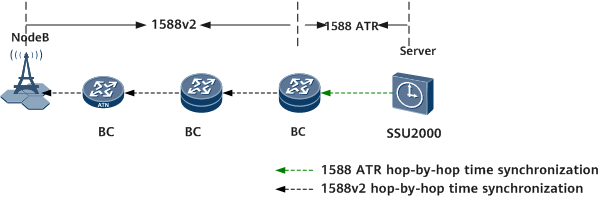

Scenario Description
- Time synchronization is required between NodeBs and the time server.
- The time server (for example, the SSU2000) only supports the 1588v2 unicast negotiation mode.
- A client first sends a negotiation request to the server, which sends time synchronization packets back to the client only after the negotiation relationship is established.
Solution Description
- You can configure the 1588 ATR hop-by-hop mode to interconnect the client with the time server in order to implement time synchronization in 1588v2 unicast negotiation mode. The client then functions as a BC to provide the time synchronization service for downstream NodeBs.
Lightweight Time Synchronization
Figure 3 Lightweight time synchronization
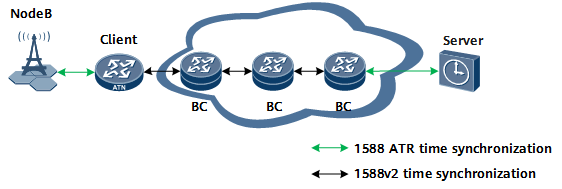

Scenario Description
- Time synchronization is required between NodeBs and the time server.
- Several devices on the network do not support 1588v2 time synchronization.
Solution Description
- With a lightweight clock deployed, lightweight time synchronization implements automatic identification and switching within a device, lowering the requirements for time synchronization precision. The system preferentially uses hop-by-hop 1588v2 time synchronization in In-situ Flow Information Telemetry (iFIT) delay measurement scenarios. Hop-by-hop 1588v2 time synchronization requires that all devices on the network support 1588v2 in order to achieve delay measurement in the sub-microsecond range. If some devices on the network do not support 1588v2, you can enable lightweight and sub-millisecond-level time synchronization on downstream devices to achieve delay measurement in the sub-millisecond range.

Lightweight clocks do not need to be configured in non-iFIT scenarios as doing so will impact time synchronization precision.