Principles of 1588 ATR
1588 ATR is used to deliver time synchronization between clock clients and clock servers.
After clock links are established through negotiation between clients and servers, 1588 ATR uses PTP packets in Layer 3 unicast mode to obtain the clock difference between clients and servers and then implement time synchronization based on the difference.
Synchronization Process
After negotiation is complete, 1588 ATR servers exchange PTP packets with clients to implement time synchronization.
1588 ATR clock synchronization is implemented in two-way mode.
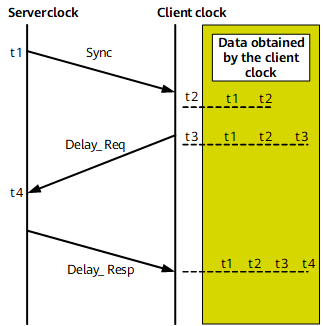
The server sends a Sync packet carrying timestamp t1 to the client.
The client receives the Sync packets at timepoint t2.
The client sends a 1588 delay_req packet carrying timestamp t3 to the server.
The server receives the 1588 delay_req packet at timepoint t4 and then generates a Delay_Rep packet and sends it to the slave clock.
The round-trip latency of the link between the server and client is (t4-t1)-(t3-t2). 1588 ATR requires the same link latency on two links involved in the same round trip. Therefore, the offset of the client is [(t2 - t1) -(t4 - t3)]/2, compared to the time of the server. The client then uses the calculation result to adjust its local time.
Layer 3 Unicast Negotiation Mechanism
Enable Layer 3 unicast negotiation before 1588 ATR time synchronization is performed. The implementation of Layer 3 unicast negotiation is as follows:
A client initiates a negotiation request with a server. The server replies with an authorization packet to implement handshake. After the handshake succeeds, the client and server establish a clock link through Layer 3 unicast packets. Then, the client and server exchange PTP packets to implement time synchronization over the clock link.
Master/Slave Server Protection Mechanism
1588 ATR supports the master/slave server protection mechanism.
A client supports negotiation with two servers and queries the negotiation result on a regular basis. If either of the servers fails after time synchronization, the client discovers the change of the negotiation status and automatically switches services to the other server. This implementation achieves service protection between the two servers.
If only one server is configured, the client attempts to re-negotiate with the server once the negotiation fails.
Duration Mechanism
A 1588 ATR client supports the duration specified in Announce, Sync, and Delay Resp packets. The duration can be placed to the TLV field in Signaling packets before they are sent to the server.
In normal situations, a client initiates a re-negotiation to a server before the duration expires so that the server can continue providing synchronization with the client.
If a client becomes Down, it cannot initiate a re-negotiation. After the duration collapses, the server does not send synchronization packets to the server any more.
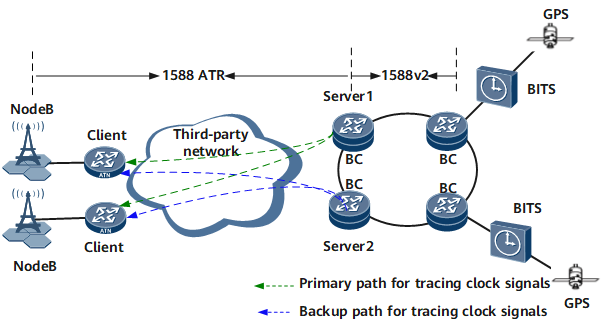
Per-hop BC + Server
1588 ATR servers can synchronize time synchronization with upstream devices and send the time source information to clients.