Packet Exchanges Involved in Dynamic Address Pool Implementation
A BRAS can interact with a RADIUS server immediately after the BRAS has a dynamic address pool configured.
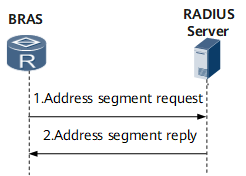
Address Segment Request (BRAS)
After having a dynamic address pool configured, the BRAS sends an address segment request to the RADIUS server. The request carries the user name, password, and suggested mask length.
Upon receipt of the request, the RADIUS server verifies the validity of the user information based on request information. The RADIUS server then assigns an address segment to the BRAS based on the suggested mask length or according to its local address segment assignment policy.
Upon receipt of the assigned address segment, the BRAS assigns addresses to users.
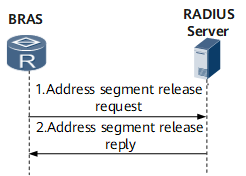
Address segment release (BRAS)
After the BRAS detects that its dynamic address pool's address usage falls below the specified lower threshold, the BRAS sends an address segment release request to the RADIUS server. The release request carries the user name, password, and target address segment.
Upon receipt of the release request, the RADIUS server releases the address segment and returns an ACK message. Upon receipt of the ACK message, the BRAS deletes the configurations of the released address segment.
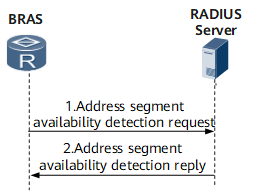
Address Segment Availability Detection (BRAS)
The BRAS periodically sends a detection request to the RADIUS server to detect the availability of an obtained address segment. The detection period is configurable. If the RADIUS server allows the BRAS to continue using the address segment, the RADIUS server sends a detection success packet in response. Otherwise, the RADIUS server sends a detection deny packet in response.
If the RADIUS server does not respond, the BRAS retransmits the detection request. If the RADIUS server still does not respond after the BRAS retransmits the detection request for a specified number of times, the BRAS sends an address segment release request to the RADIUS server. If the BRAS receives a response from the RADIUS server, the BRAS immediately releases the address segment. If the BRAS does not receive any response, the BRAS releases the address segment after its local timer expires.
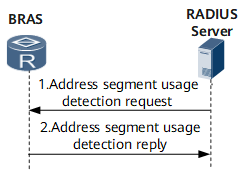
Address Segment Usage Detection (RADIUS Server)
The RADIUS server sends a COA packet that carries the user name, start address of the assigned address segment, and mask length to the BRAS. Upon receipt of the packet, the BRAS checks whether this address segment is in use.
If the RADIUS server receives an ACK packet from the BRAS, the RADIUS server immediately releases the address segment. If the RADIUS server receives a non-ACK packet, the RADIUS server does not release the address segment. If the BRAS does not respond, the RADIUS server retransmits the COA packet. If the BRAS still does not respond after the RADIUS server retransmits the COA packet for a specified number of times, the address segment needs to be manually released on the RADIUS server.