Basic Process of the IEEE 802.1x Authentication System
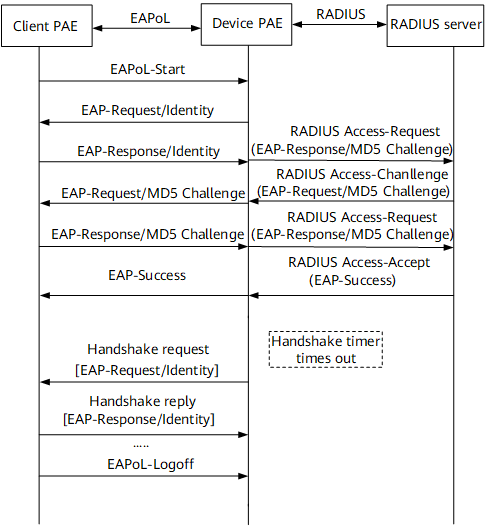
Basic process of the IEEE 802.1x authentication system (1)
This part takes EAP packet relaying on the device PAE as an example. Figure 1 shows the basic process of the IEEE 802.1x authentication system. Being a relay device, the BRAS converts EAPoL packets from the user into EAPoR packets and sends them to the RADIUS server. In addition, the BRAS converts EAPoR packets from the RADIUS server into EAPoL packets and sends them to the user. During authentication, the BRAS transparently transmits user packets until it receives an Access-Accept packet from the RADIUS server, which indicates a successful user access.
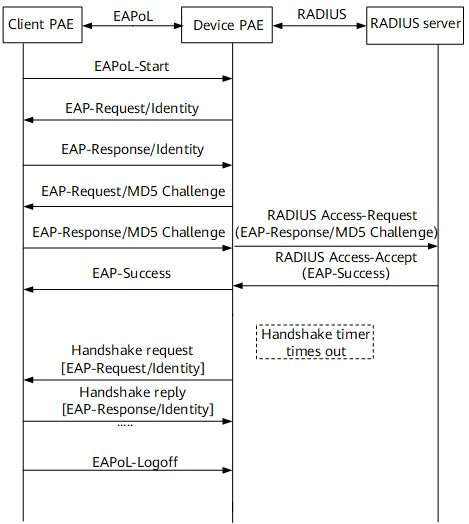
Basic process of the IEEE 802.1x authentication system (2)
This part takes EAP packet terminating and mapping into CHAP packets on the device PAE as an example. Figure 2 shows the basic process of the IEEE 802.1x authentication system. The BRAS terminates EAP packets and converts them into standard RADIUS packets and sends an authentication request to the RADIUS server. Generally, this process is applicable to access authentication in the situation where the RADIUS server does not support the EAP attribute.