What Is Load Balancing
Load balancing means that network nodes distribute traffic among multiple links during transmission. Route load balancing, tunnel load balancing, and trunk load balancing are available.
Route Load Balancing
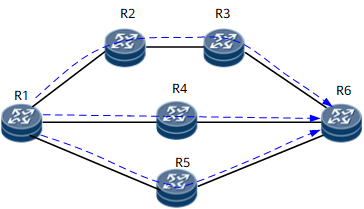
Route load balancing means that traffic is load-balanced over multiple forwarding paths to a destination, as shown in Figure 1.
If the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) of a device has multiple entries with the same destination address and mask but different next hops, outbound interfaces, or tunnel IDs, route load balancing can be implemented.

Route load balancing can be implemented in either of the following solutions:
- Solution 1: Configure multiple equal-cost routes with the same destination network segment but different next hops and the maximum number of equal-cost routes for load balancing. This solution is mostly used among links that directly connect two devices. However, this solution is being replaced with the trunk technology as the trunk technology develops. Compared with this solution, the trunk technology saves IP addresses and facilitates management by bundling links into a trunk.
- Solution 2: Separate destination IP addresses into several groups and allocate one link for each group. This solution improves the utilization of bandwidth resources. However, if you use this solution to implement load balancing, you must observe and analyze traffic and know the distribution and trends of traffic of various types.
Tunnel Load Balancing
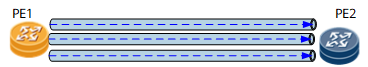
Tunnel load balancing is applicable when the ingress PE on a VPN has multiple tunnels to a destination PE, as shown in Figure 2. Traffic can be load-balanced among these tunnels.
Trunk Load Balancing
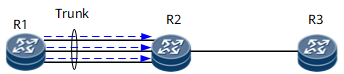
Trunk load balancing means that traffic is load-balanced among trunk member links after multiple physical interfaces of the same link layer protocol are bundled into a logical data link, as shown in Figure 2.
Load Balancing Characteristics
Advantages:
- Load balancing distributes traffic among multiple links, providing higher bandwidth than each individual link and preventing traffic congestion caused by link overload.
- Links used for load balancing back up each other. If a link fails, traffic can be automatically switched to other available links, which increases link reliability.
Disadvantages:
Traffic is load-balanced randomly, which may result in poor traffic management.