Load Balancing Among Static Routes
Conditions
When the maximum number of static routes that load-balance traffic and the maximum number of routes of all types that load-balance traffic are both greater than 1, the following rules apply:
- If N active static routes with the same prefix are available and N is less than or equal to the maximum number of static routes that can be used to load-balance traffic, traffic is load-balanced among the N static routes, regardless of whether they have the same cost.
- If a static route is active and has N iterative next hops, traffic is load-balanced among N routes, which is called iterative load balancing.

Black-hole routes cannot be used for load balancing.
In Figure 1, R1 learns two OSPF routes to 10.1.1.2/32, both with the cost 2. The outbound interface and next hop of one route are GE 0/1/0 and 10.1.1.34, and the outbound interface and next hop of the other route are GE 0/1/8 and 10.1.1.38.

Interfaces 1 and 2 in this example represent GE 0/1/0, and GE 0/1/8, respectively.
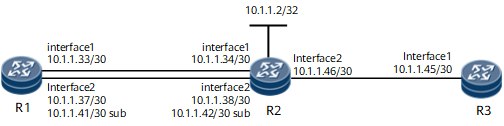
A static route is configured on R1 using the following command:
ip route-static 10.1.1.45 30 10.1.1.2 inherit-cost
Although only one static route is configured, two iterative next hops (10.1.1.34 and 10.1.1.38) are available. Therefore, the number of static routes displayed in the routing table is 1, but the number of FIB entries is 2.
- If another static route is configured on R1 using the following command:
ip route-static 10.1.1.45 30 10.1.1.42
Traffic is load-balanced among three routes, although the cost of the new static route is different from that of the other two routes.
- If the following command is run to set the priority of the new static route to 1:
ip route-static 10.1.1.45 30 10.1.1.42 preference 1
R1 will preferentially select the static route with next hop 10.1.1.42. As a result, the other static routes become invalid, and traffic is no longer load-balanced.