ECMP Load Balancing Consistency
Equal-Cost Multi-Path routing (ECMP) implements load balancing and link backup. ECMP applies to networks where the same destination address can be reachable through multiple different links. Without the use of ECMP, packets destined for this destination address can be forwarded through only one link, while other links are in backup state or invalid, and link switching in the case of dynamic routes requires a specified period of time. ECMP ensures that the packets are forwarded through multiple links, increasing transmission bandwidth and providing data transmission without delay or packet loss.
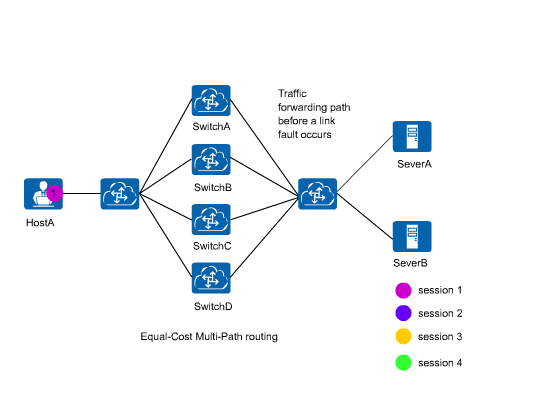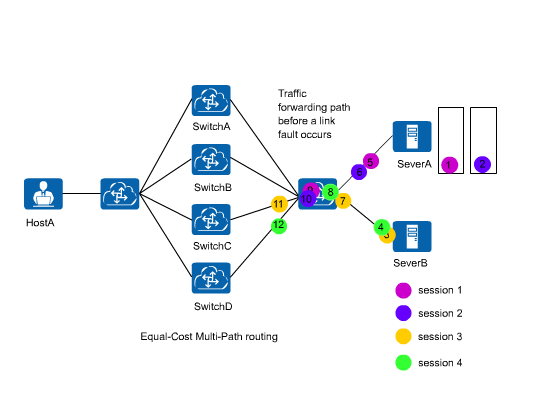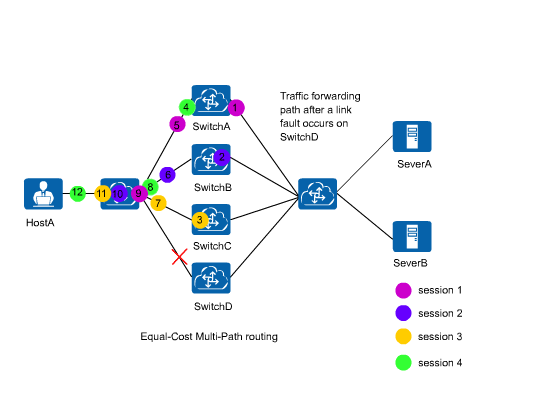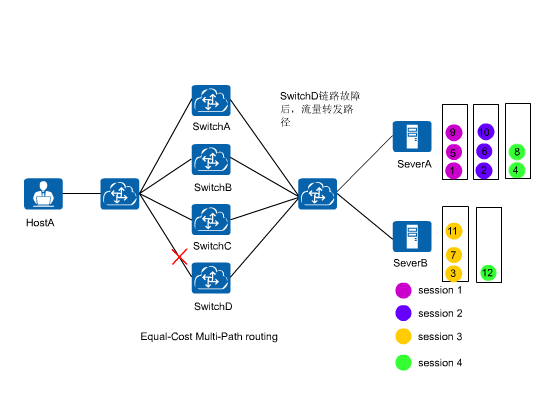
In an ECMP scenario shown in Figure 1, when a link fails, all traffic will be load balancing again using the hash algorithm to prevent traffic interruption. All the traffic will then be load balanced among normal links. As a result, traffic forwarding paths may change. Requests of the same user may be sent to different servers, greatly affecting the services in which sessions need to be maintained.
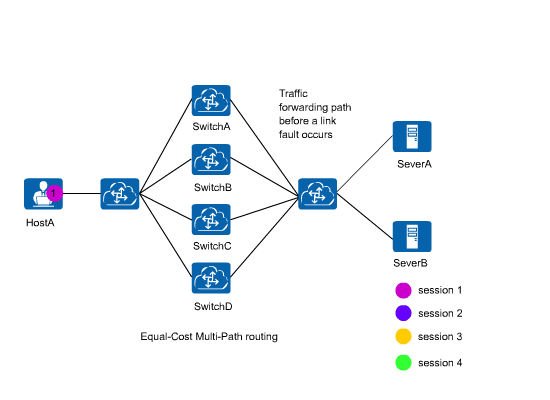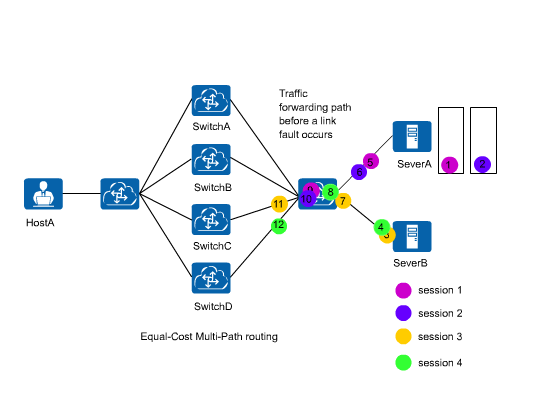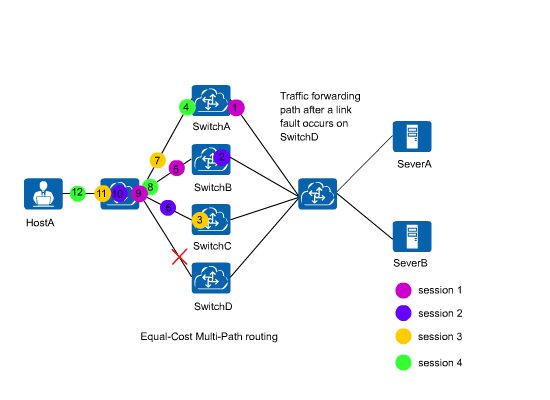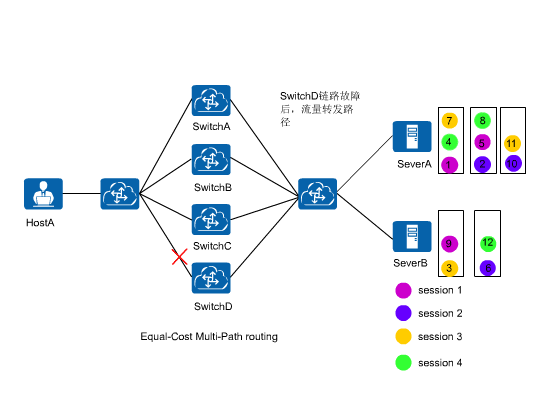
ECMP load balancing consistency function provides a method to solve the preceding problem. In Figure 2, this function enables hash calculation to be performed only for traffic on the faulty link, without affecting traffic on other normal links. This function maintains service sessions on normal links.